How to read tax transcript for refund (2024)

Struggling to decode your business tax transcript for a refund? You’re not alone. Many entrepreneurs find these documents baffling, leading to delays in accessing their hard-earned money. Frustration mounts as you navigate through complex jargon and endless numbers. But fear not, as this article holds the key to your solution.
We’ll demystify the tax transcript, providing step-by-step guidance that simplifies the process. With our help, you’ll confidently decipher the numbers and ensure your refund reaches your business swiftly. Say goodbye to confusion and hello to your well-deserved funds with this straightforward guide.
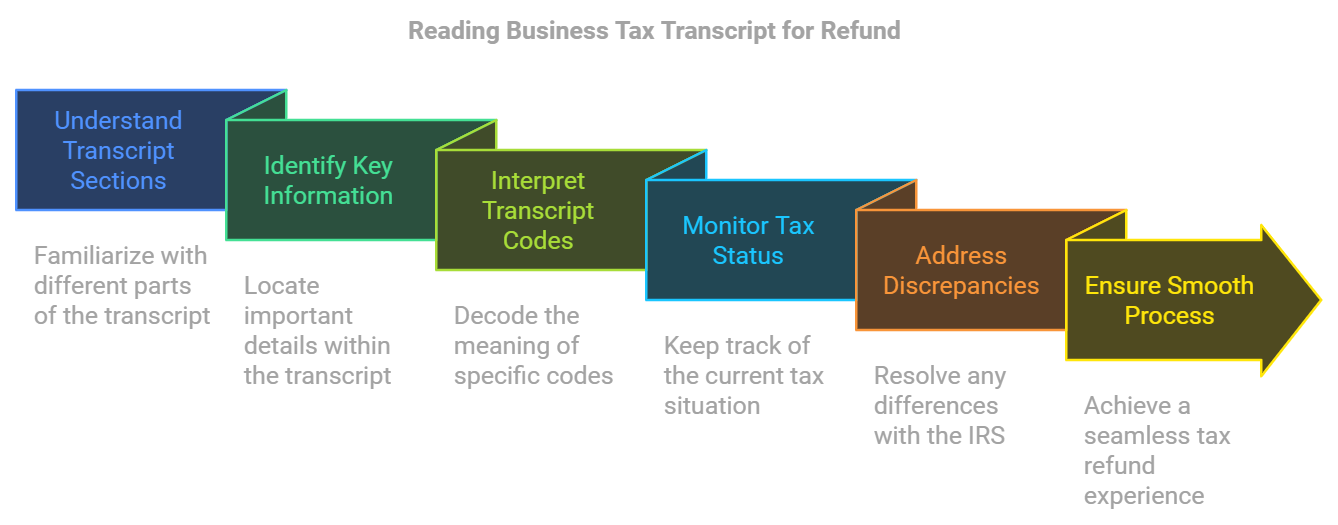
Table of Contents
What is a tax transcript?
A business tax transcript is a document from the IRS that shows a company’s tax-related information. It provides a summary of the tax returns a business has filed, including income, deductions, and credits. This transcript is useful for various purposes, such as verifying financial information for loans, mortgages, or government contracts. It’s obtained directly from the IRS and contains important details, like the employer identification number, tax return type, and filing dates. Business owners can request these transcripts online, by mail, or through the phone. This document helps ensure financial transparency and compliance with tax regulations, benefiting both businesses and government agencies.
Why is it important to read your tax transcript if you are a business owner?
1. Avoid Costly Mistakes
Reading your tax transcript is essential for business owners to avoid costly mistakes. When you receive your transcript, it provides a detailed record of your financial information reported to the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). By reviewing it, you can identify any errors or discrepancies in your tax filings. These errors could result in overpayment, underpayment, or even penalties and interest charges. For a business owner, financial accuracy is paramount, and examining your tax transcript helps ensure your filings are error-free.
2. Verify Income Accuracy
One of the key reasons for business owners to read their tax transcript is to verify the accuracy of reported income. The transcript provides a summary of all income sources associated with your business. It includes data from various forms such as the W-2, 1099, and Schedule K-1. By carefully examining this information, you can confirm that your income is correctly documented. If there are any discrepancies, it’s crucial to address them promptly to prevent potential tax audits and penalties.
3. Detect Potential Identity Theft
Business owners should be vigilant about identity theft, as it can have severe consequences for their finances and personal information. Reviewing your tax transcript helps you detect any suspicious activity. If you notice income sources or filings that you don’t recognize, it may be a sign of identity theft. Addressing such issues early can protect your business and personal financial information from unauthorized access and fraudulent tax filings.
4. Understand IRS Assessments
Your tax transcript also includes information about IRS assessments and adjustments. These assessments may be made when the IRS identifies discrepancies or inconsistencies in your tax filings. It’s essential to read your tax transcript to understand these assessments. If you disagree with the IRS’s findings, you can take appropriate action by filing an appeal or providing additional documentation. Ignoring these assessments can lead to increased tax liabilities, so business owners should stay informed and take action as needed.
5. Plan for the Future
Reviewing your tax transcript is not just about correcting past mistakes; it also helps you plan for the future. By analyzing your financial history, you can make informed decisions for your business’s financial health. This includes setting aside funds for tax payments, making necessary adjustments to your business operations, and ensuring compliance with tax regulations. Understanding your tax transcript equips you with valuable insights that can aid in making strategic financial choices and staying in good standing with the IRS.
How to obtain your tax transcript
Obtaining your business tax transcript is a crucial task for any business owner. Whether you need it for tax compliance, loan applications, or financial planning, this guide will walk you through the simple steps to get your business tax transcript quickly and efficiently.
Step 1: Gather Required Information
Before you start the process, ensure you have the necessary information ready. You’ll need your Employer Identification Number (EIN), business name, and address. This data is vital to verify your identity.
Step 2: Visit the IRS Website
Go to the official website of the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) at www.irs.gov. The IRS provides an online tool for obtaining your business tax transcript, which is free of charge.
Step 3: Access the Online Tool
Once on the IRS website, locate the “Get Your Tax Record” tool. This tool will guide you through the process of obtaining your tax transcript.
Step 4: Choose the Transcript Type
Select the type of transcript you need. In most cases, you’ll want the “Tax Return Transcript.” This provides a summary of your return, which is typically sufficient for most purposes.
Step 5: Verify Your Identity
The IRS will ask you to provide personal and business information to confirm your identity. Make sure to enter accurate data to avoid any delays in the process.
Step 6: Request the Transcript
After identity verification, you can request your tax transcript. The IRS will provide an option to download and print it instantly, or you can receive it by mail within a few business days.
Step 7: Save and Store Your Transcript
Once you’ve obtained your tax transcript, it’s essential to save it for your records. You might need it for future tax filings or financial transactions, so keep it in a safe place.
Obtaining your business tax transcript doesn’t have to be a complex process. By following these simple steps and utilizing the IRS’s online tool, you can access the information you need to keep your business running smoothly and in compliance with tax regulations.
How to read your tax transcript for refund

Understanding the different sections of your tax transcript
When you receive your business tax transcript, it will contain vital information about your tax return and financial history. There are three main types of tax transcripts: the Account transcript, Return transcript, and Record of account transcript.
Account transcript
The Account transcript provides a summary of your business’s financial activities, including payments and credits. It shows the balance of your account, any penalties assessed, and interest accrued. This transcript gives you a snapshot of the current state of your tax account.
Return transcript
The Return transcript provides detailed information about your filed tax return, including the forms and schedules attached. It also shows your adjusted gross income, filing status, and the types and amounts of income, deductions, and credits you reported.
Record of account transcript
The Record of account transcript is a combination of both the Account and Return transcripts. It offers a comprehensive overview of your financial history and filed tax returns. It’s particularly useful when you need to review your tax return history or verify past tax payments.
Identifying key information on your tax transcript
To effectively read your business tax transcript, look for key information that can impact your financial situation and tax refund.
Your business name and taxpayer identification number (TIN)
Your business name and TIN should be prominently displayed on the transcript. Ensure they match the information you provided when filing your taxes. Any discrepancies can lead to complications, including delayed refunds.
The type of tax return you filed
Check for the specific type of tax return you filed, such as a corporate tax return (Form 1120) or a partnership tax return (Form 1065). This information ensures you’re examining the correct document.
Your taxable income
Identify your business’s taxable income, which is crucial for determining your tax liability or refund amount. This figure reflects your gross income minus deductions and credits.
Any tax credits or deductions you claimed
Review your transcript for details on tax credits or deductions you claimed. These can significantly affect your final tax liability and the amount of your refund.
The amount of tax you owe or the amount of your refund
The most critical piece of information on your tax transcript is the amount of tax you owe or the amount of your refund. If you are owed a refund, you’ll find this figure on the transcript. If you owe taxes, it will indicate the outstanding amount.
How to identify and interpret transcript codes
Within your tax transcript, you’ll find various codes that provide detailed information about your tax return and any associated actions taken by the IRS.
Common transcript codes for businesses
Familiarize yourself with common transcript codes relevant to businesses. For example, Code 150 indicates that your return has been filed, while Code 806 indicates that a refund has been applied to an outstanding debt. Understanding these codes helps you interpret your transcript accurately.
How to read refund transcript codes
If you’re interested in tracking your refund, focus on codes related to refunds. Code 846 signifies a refund has been issued, and Code 766 shows the amount applied to a prior tax year. These codes provide insights into the status and history of your refund.
What does a tax transcript look like
Here’s what a tax transcript generally includes, depending on the type:
1. Tax Return Transcript
- Purpose: Summarizes the tax return filed.
- Contents:
- Taxpayer’s name and address
- Filing status (e.g., single, married filing jointly)
- Adjusted Gross Income (AGI)
- Taxable income
- Credits and deductions
- Payments and refunds
- Line-by-line information from the original tax return (Form 1040, 1040A, or 1040EZ), excluding any changes made after filing.
- Format: Usually 1-3 pages.
2. Tax Account Transcript
- Purpose: Shows basic tax account data, including return type, filing status, and any adjustments made by the IRS.
- Contents:
- Tax year
- Total tax reported
- Adjustments made
- Balance owed or refund amount
- Format: Focuses more on account activities rather than return details.
3. Record of Account Transcript
- Purpose: Combines the Tax Return Transcript and Tax Account Transcript into a single document.
- Contents: A comprehensive view of both the tax return data and any changes made after filing.
- Format: Can be longer due to the combined data.
4. Wage and Income Transcript
- Purpose: Lists data from W-2s, 1099s, 1098s, and other informational forms reported to the IRS.
- Contents:
- Employer or payer names
- Income amounts
- Withheld taxes
- Format: Useful for reconstructing tax returns or verifying income.
5. Verification of Non-Filing Letter
- Purpose: Confirms that the IRS has no record of a filed tax return for a specific year.
- Contents:
- Taxpayer’s name
- Confirmation of non-filing
- Format: Simple and concise.
Appearance
- Tax transcripts are generally presented in a plain, text-heavy format.
- They are issued electronically (PDF) or on paper, with sections clearly labeled for easy navigation.
- No graphics, logos, or design elements are included—strictly IRS-formatted text.
Using your tax transcript to track your refund
Your tax transcript can be a valuable tool to track the progress of your refund and identify potential issues that might cause delays.
How to check the status of your refund
To track your refund, visit the IRS website and use the “Where’s My Refund?” tool. You’ll need to input your Social Security Number or TIN, your filing status, and the exact refund amount as shown on your tax return. This tool will provide you with the most up-to-date information on your refund status.
What to do if your refund is delayed
If your refund is delayed, your tax transcript can help you identify the underlying issues. Check for codes that indicate a delay or the need for additional information, such as Code 570, which may signal a freeze on your refund. Contact the IRS promptly to resolve any problems and expedite your refund.
Negative Refund Amount on a Tax Transcript
A negative refund amount on a tax transcript indicates that the taxpayer owes money to the IRS rather than being owed a refund. Here’s how it works:
- Refund Amount: This section shows whether the taxpayer is due a refund or has a balance due.
- Positive Value: A refund the taxpayer will receive.
- Negative Value (e.g., “-$500”): The taxpayer owes the IRS $500.
Example: Negative Refund Amount
Refund Amount: -$500
This means the taxpayer’s total tax liability exceeded their payments and credits by $500. They must pay this amount to the IRS.
Negative Account Balance on an IRS Transcript
A negative account balance on an IRS transcript is a good sign—it means the IRS owes money to the taxpayer. This balance reflects overpayments, refunds not yet processed, or credits carried over from previous years.
- Account Balance:
- Positive Value: Amount the taxpayer owes to the IRS.
- Negative Value (e.g., “-$1,200”): Amount the IRS owes the taxpayer.
Example: Negative Account Balance
Account Balance: -$1,200
This indicates the IRS owes the taxpayer $1,200, which could be pending as a refund or carried forward for future tax liabilities.
Conclusion
In conclusion, reading your business tax transcript for a refund can be straightforward when you understand the different sections, identify key information, and interpret transcript codes accurately. By keeping a close eye on your tax transcript, you can stay informed about your tax status and take appropriate action if your refund is delayed. Remember that maintaining accurate records and promptly addressing any discrepancies with the IRS can help ensure a smooth tax refund process for your business.


