Corporate Tax in UAE: A Complete (In-Depth) Guide

Understanding corporate tax in UAE is essential for businesses operating within the country, whether you’re a startup, an SME, or a multinational corporation. With the recent changes to the United Arab Emirate’s tax landscape, including the introduction of a corporate tax rate and various tax exemptions, it is crucial to stay informed about the latest regulations and filing requirements.
The UAE’s tax policies are designed to foster economic growth, encourage foreign investment, and ensure compliance with global tax standards, making it vital for businesses to adapt to these new frameworks. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the key aspects of corporate tax in the UAE, including registration, filing procedures, tax exemptions, and strategies for minimizing tax liabilities.
Understanding Corporate Tax Laws in the UAE
Corporate tax is a significant financial consideration for businesses operating in the UAE. Introduced as part of the UAE’s commitment to aligning with international standards, corporate tax impacts both local companies and foreign entities conducting business in the region.
What is Corporate Tax in UAE?
Corporate tax in UAE is a direct tax levied on the profits of businesses. The law came into effect to diversify the country’s revenue sources beyond oil. While the UAE remains an attractive hub due to its competitive tax structure, businesses must comply with new regulations.
Who Must Register for Corporate Tax?
Businesses that generate taxable income above the exemption threshold must register with the Federal Tax Authority (FTA). Failure to comply can lead to penalties.
1. Are small businesses affected by corporate tax?
Small businesses earning less than AED 375,000 in profits are exempt from corporate tax.
2. How does the UAE compare globally in tax competitiveness?
With a flat 9% tax rate, the UAE offers one of the most business-friendly tax regimes worldwide.
The Legal Framework for Corporate Tax in UAE
The introduction of corporate tax in the United Arab Emirates represents a significant step toward aligning with global tax practices. This legal framework is designed to ensure transparency, fairness, and compliance while supporting the country’s vision for sustainable economic growth. Here’s an in-depth look at the legal structure governing corporate tax UAE.
Understanding the Corporate Tax Law
The Federal Decree-Law No. 47 of 2022 governs United Arab Emirates corporate tax. It outlines the scope, rates, exemptions, compliance requirements, and penalties for non-compliance. This law came into effect for financial years beginning on or after June 1, 2023.
Key Legal Provisions
The law’s structure provides clarity on the application of corporate tax:
| Legal Aspect | Details |
| Taxable Persons | Includes UAE-incorporated companies, branches of foreign companies, and natural persons engaged in business. |
| Exemptions | Government entities, public benefit organizations, investment funds, and qualifying free zones. |
| Tax Rates | 0% for taxable income up to AED 375,000; 9% for income above AED 375,000. |
| Qualifying Free Zone Income | Subject to 0% tax if certain conditions are met. |
| Deductible Expenses | Business expenses wholly and exclusively incurred for taxable purposes. |
| Transfer Pricing Compliance | Entities must follow arm’s length principles and maintain documentation. |
Objectives of the Legal Framework
- Economic Diversification: Reduce reliance on oil revenues by broadening the tax base.
- Global Integration: Ensure UAE tax laws align with international tax standards like the OECD’s BEPS framework.
- Compliance and Governance: Promote a transparent and well-regulated business environment.
Compliance and Registration Obligations
1. Tax Registration
All businesses subject to corporate tax must register with the Federal Tax Authority (FTA). The registration deadline varies based on the financial year-end.
2. Filing Tax Returns
Taxpayers must file their returns annually, supported by audited financial statements.
3. Documentation
Businesses must maintain detailed records of income, expenses, and tax calculations for a minimum of five years.
Penalties for Non-Compliance
The legal framework includes strict penalties to deter non-compliance:
| Type of Violation | Penalty |
| Failure to register for corporate tax | AED 10,000 (minimum), increasing with repeated offenses. |
| Failure to file tax returns on time | AED 1,000 for the first offense, escalating for delays. |
| Incorrect reporting | Penalties based on the severity and nature of the misrepresentation. |
Impact on Different Business Sectors
The legal framework ensures a level playing field across industries but considers unique sector-specific circumstances. For example:
- Real Estate: Companies involved in real estate leasing and development must evaluate income streams for taxable elements.
- SMEs: Businesses below the AED 375,000 profit threshold are exempt but must monitor income growth.
How to Stay Compliant
- Regularly review the legal requirements and updates from the FTA.
- Seek professional advice to navigate complex tax laws.
- Implement robust financial management systems to ensure accurate reporting.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can non-resident businesses be subject to UAE corporate tax?
Yes, non-residents earning UAE-sourced income may be taxed under the law.
2. Is corporate tax applicable to free zone companies?
Free zone companies can enjoy a 0% rate if they meet the conditions for qualifying income.
3. What happens if a business doesn’t comply?
Non-compliance can result in penalties, audits, and potential business disruptions.
UAE Corporate Tax Rates Explained
The UAE’s corporate tax regime is designed to maintain the country’s competitive edge as a business hub while meeting global taxation standards. The tax rates introduced are straightforward and aim to ease the compliance burden for businesses. This guide breaks down the UAE corporate tax rates and how they apply to various entities.
Corporate Tax Rates Overview
The corporate tax rates in the UAE are structured to support small businesses while ensuring fair taxation of larger entities:
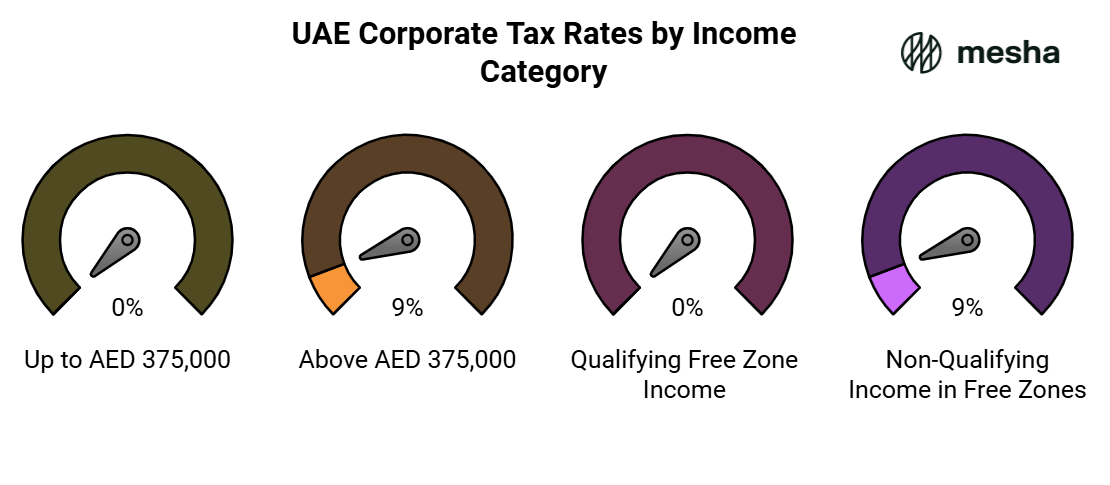
| Taxable Income | Corporate Tax Rate |
| Up to AED 375,000 | 0% |
| Above AED 375,000 | 9% |
| Qualifying Free Zone Income | 0% (subject to meeting specific conditions) |
| Non-Qualifying Income in Free Zones | 9% |
Key Points About United Arab Emirates Corporate Tax Rates
- Small Business Support
Income below AED 375,000 is exempt from tax, allowing small businesses and startups to thrive without immediate tax pressures. - Global Competitiveness
The standard 9% rate is among the lowest in the world, making the UAE an attractive destination for multinational companies. - Free Zone Incentives
Businesses operating in free zones can enjoy a 0% tax rate on qualifying income. This maintains the UAE’s status as a hub for trade, logistics, and innovation. - Progressive Yet Simple
Unlike many countries with tiered rates, the UAE offers a flat 9% rate for taxable income above the threshold, simplifying calculations and compliance.
Examples of Corporate Tax Calculation
| Scenario | Taxable Income | Tax Rate | Tax Due |
| Small Business | AED 300,000 | 0% | AED 0 |
| Medium-Sized Enterprise | AED 500,000 | 9% on AED 125,000 | AED 11,250 |
| Large Corporation | AED 2,000,000 | 9% on AED 1,625,000 | AED 146,250 |
Note: The taxable income is calculated after deducting allowable expenses.
Checkout our corporate tax calculator for UAE
Special Cases for Tax Rates
- Free Zone Businesses
Free zone entities must adhere to specific conditions, such as conducting activities within the free zone or with foreign entities, to qualify for the 0% rate. - Multinational Corporations (MNCs)
MNCs subject to OECD’s Global Minimum Tax rules (15% for large groups) may need to pay additional taxes in their home countries. - Foreign Entities
Non-resident companies earning UAE-sourced income, such as through contracts or investments, are taxed at the 9% rate.
Comparison With Other Countries
| Country | Corporate Tax Rate | Key Notes |
| UAE | 9% | Low flat rate, free zone incentives. |
| Saudi Arabia | 20% | Higher rate for non-Saudi GCC businesses. |
| Singapore | 17% | Competitive but higher than UAE. |
| United States | 21% | Complex, with state taxes added. |
| United Kingdom | 25% (from 2023) | Higher rate to address budget deficits. |
How UAE Corporate Tax Rates Affect Businesses
- Startups: Exemption up to AED 375,000 encourages innovation and entrepreneurship.
- SMEs: The low rate allows businesses to reinvest profits and scale operations.
- MNCs: Transparent and competitive rates attract foreign direct investment.
- Free Zones: 0% rate reinforces the UAE’s position as a global trade and logistics hub.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Are there any additional taxes beyond corporate tax?
The UAE does not impose taxes like capital gains tax or withholding tax, except for a few cases under specific conditions.
2. Do corporate tax rates differ by industry?
No, the corporate tax rates apply uniformly across all industries, except for oil and gas companies subject to separate tax frameworks.
3. Can businesses in free zones mix qualifying and non-qualifying income?
Yes, but non-qualifying income will be taxed at the standard 9% rate.
What You Need to Know About UAE Corporate Tax
The introduction of UAE corporate tax has brought significant changes to the business environment. While the country remains one of the most tax-friendly jurisdictions globally, understanding corporate tax is crucial for businesses to stay compliant and optimize their operations.
Why Was Corporate Tax Introduced in the UAE?
The UAE government implemented corporate tax to achieve several strategic objectives:
- Economic Diversification: Reduce reliance on oil revenues by creating a sustainable tax base.
- Global Standards: Align with international frameworks, such as the OECD’s Base Erosion and Profit Shifting (BEPS) project.
- Transparency: Improve reporting and compliance to attract foreign investment.
Who Is Subject to Corporate Tax?
| Category | Applicability |
| UAE-Registered Companies | Taxable on worldwide income, subject to exemptions. |
| Foreign Branches in the UAE | Taxed on UAE-sourced income only. |
| Free Zone Entities | Taxable at 0% on qualifying income; 9% on non-qualifying income. |
| Individuals Engaged in Business | Only individuals running licensed businesses are subject to corporate tax. |
| Foreign Entities | Taxed on UAE-sourced income, such as contracts or real estate investments. |
What is Taxable Income?
Taxable income is calculated as the net profit reported in the financial statements, adjusted for allowable and non-allowable expenses. Some common adjustments include:
- Allowable Deductions: Salaries, office rent, utility costs, and marketing expenses.
- Non-Allowable Deductions: Fines, personal expenses, and non-business-related costs.
How Corporate Tax Benefits the UAE Economy
- Revenue Diversification: The tax provides a stable income stream for the government.
- Improved Global Perception: Adopting corporate tax boosts the UAE’s reputation as a compliant, transparent jurisdiction.
- Business Growth: Competitive rates ensure the UAE remains a preferred destination for startups and multinational corporations.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Are freelancers subject to corporate tax?
No, freelancers not operating under a commercial license are not subject to corporate tax.
2. Do free zone companies need to register for corporate tax?
Yes, even if they qualify for the 0% rate, free zone companies must register and file tax returns.
3. Is corporate tax applicable to all income earned by UAE businesses?
Corporate tax applies only to taxable income. Exemptions and deductions can significantly reduce the taxable base.
Step-by-Step Guide to Corporate Tax Registration in UAE
Corporate tax registration is a critical step for businesses operating in the UAE. Ensuring timely registration with the Federal Tax Authority (FTA) helps businesses comply with the law and avoid penalties. This guide provides a detailed overview of the corporate tax registration process.
Who Needs to Register for Corporate Tax?
Not all businesses are required to register immediately. The following entities must register for corporate tax:
- UAE Businesses: Companies incorporated in the UAE or operating through branches.
- Free Zone Entities: Businesses in free zones that meet the qualifying income criteria.
- Foreign Businesses: Companies earning UAE-sourced income.
- Individuals with a Business License: Individuals conducting commercial activities under a trade license.
Exempt entities such as government bodies, investment funds, and public benefit organizations do not need to register unless specified.
Step-by-Step Corporate Tax Registration Process
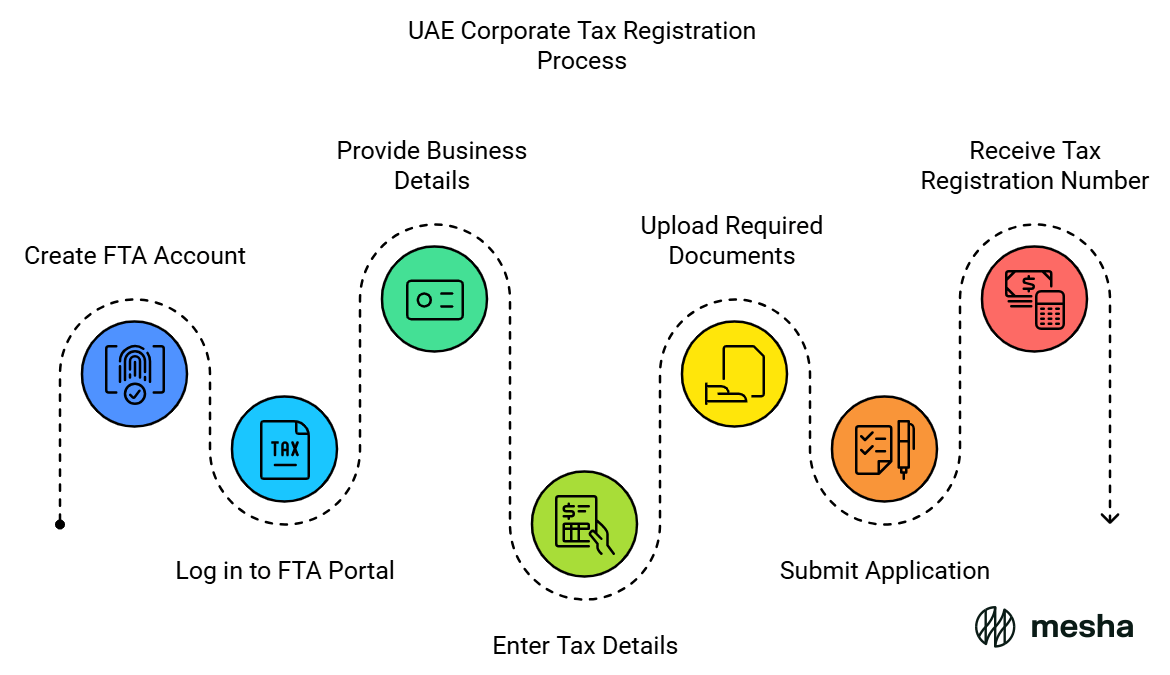
- Create an FTA Account
- Visit the Federal Tax Authority’s official website (www.tax.gov.ae).
- Create an account by providing your email address and setting up login credentials.
- Log in to the FTA Portal
Use your registered email and password to access the corporate tax registration section. - Provide Basic Business Details
- Enter the trade license details, including the license number and issuing authority.
- Provide the company’s legal name and address.
- Specify the legal structure (e.g., LLC, branch, free zone entity).
- Enter Tax Details
- Declare the financial year start and end dates.
- Indicate whether the entity qualifies for exemptions or falls under a free zone regime.
- Upload Required Documents
Ensure you have the following documents ready:- Trade license copy
- Passport and Emirates ID of owners (for individual businesses)
- Memorandum of Association (MOA) or Articles of Association (AOA)
- Proof of business activities
- Submit the Application
After completing the required fields and uploading documents, review your details and submit the application. - Receive Tax Registration Number (TRN)
Upon successful registration, you will receive a Tax Registration Number (TRN). This number must be quoted in all corporate tax filings.
Registration for Free Zone Entities
Free zone businesses must also register for corporate tax, even if they qualify for the 0% rate. These entities should ensure that their qualifying income is clearly documented to avoid complications during audits.
What Happens After Registration?
Once registered, businesses must:
- File annual corporate tax returns.
- Maintain financial records for a minimum of five years.
- Regularly check for updates or changes in tax laws on the FTA portal.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Late Registration: Delays can lead to penalties. Register as soon as you meet the eligibility criteria.
- Incomplete Information: Providing inaccurate or incomplete details can result in rejected applications.
- Assuming Exemption: Always confirm whether your business qualifies for exemption by reviewing the FTA guidelines.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is there a fee for registering for corporate tax?
No, registration with the FTA is free.
2. Can a business register before earning taxable income?
Yes, businesses are encouraged to register as soon as they meet the eligibility criteria, even if taxable income is yet to be generated.
3. Are free zone companies required to register if they qualify for 0% tax?
Yes, free zone companies must register regardless of whether their income is taxed at 0%.
Corporate Tax Exemptions in the UAE: Who Qualifies?
The UAE corporate tax regime is designed to support businesses, with specific exemptions aimed at fostering investment and economic growth. Understanding who qualifies for corporate tax exemptions is key for businesses to optimize their tax positions and remain compliant.
Entities Exempt from Corporate Tax
The UAE provides exemptions for several categories of entities. These exemptions are designed to encourage investment, support specific sectors, and maintain a favorable business environment. The main exempt entities include:
| Entity Type | Exemption Criteria |
| Government Entities | Fully exempt, as these are not engaged in commercial business operations. |
| Public Benefit Organizations | Exempt if their activities are deemed to benefit the public (subject to approval). |
| Investment Funds | Exempt if they meet specific criteria outlined by the FTA, such as being registered. |
| Pension and Social Security Funds | Exempt to ensure long-term stability for workers. |
| Charitable Organizations | Exempt if their operations are recognized as non-profit and public-oriented. |
Free Zone Entities and Their Exemption Criteria
Free zone companies are granted a 0% corporate tax rate on qualifying income. However, to benefit from this exemption, businesses must meet specific requirements set by the Federal Tax Authority (FTA):
- Conducting Activities Within the Free Zone
Free zone companies must conduct their core business activities within the designated free zone area. - Engagement in International Trade
Free zone entities that deal exclusively with foreign clients and international markets are more likely to qualify for exemptions. - Meeting FTA Compliance Criteria
To ensure transparency, businesses must adhere to FTA’s economic substance regulations. This may include maintaining adequate staff, office space, and conducting real business activities.
Income Qualifying for Exemption
Certain types of income are generally exempt from corporate tax, as long as the business meets the necessary criteria. These include:
- Income from International Trade
This applies to businesses operating in free zones or those engaged in export-oriented trade. Income generated from activities such as sales to foreign clients or international logistics can qualify for tax exemptions. - Dividend and Capital Gains Income
Income derived from the sale of shares in other companies or dividends from qualifying investments may be exempt. - Income from Government Contracts
Businesses that earn income solely from government contracts may also be eligible for tax exemptions.
How to Apply for Exemption
To apply for tax exemptions, businesses must register with the Federal Tax Authority (FTA) and provide the following documents as part of the exemption process:
- Proof of Business Activities
Companies must submit documentation proving that their activities align with the exemption criteria, such as contracts and income sources. - Tax Registration
Businesses must still register with the FTA to be officially recognized and ensure they are complying with the law. - Regular Documentation
Free zone companies and other entities seeking exemptions must maintain proper accounting records and submit financial statements to the FTA.
Corporate Tax Exemption for SMEs
Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) can also benefit from specific tax relief measures under the UAE’s corporate tax laws. Businesses with taxable income up to AED 375,000 are not subject to corporate tax. This exemption allows SMEs to focus on growth without the burden of tax obligations during their initial phases of operation.
Other Notable Exemptions
- Research and Development (R&D)
Companies involved in innovation, research, and technological development may qualify for tax relief under specific government incentives aimed at encouraging scientific advancement. - Real Estate Investment
Real estate companies may qualify for exemptions if they meet the requirements for foreign investments or operate under certain conditions. This ensures the United Arab Emirates remains an attractive destination for global real estate investors. - Education and Healthcare Sectors
Businesses in the education and healthcare industries may be granted exemptions, provided they are not-for-profit or meet the regulations set by the government.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Are all businesses in free zones exempt from corporate tax?
No, only those that meet specific criteria related to the type of income earned, and activities carried out within the free zone.
2. Can a company lose its exemption status?
Yes, a company can lose its exemption status if it fails to comply with FTA regulations or does not meet the necessary requirements for qualifying income.
3. Are real estate companies fully exempt from corporate tax?
Real estate companies may qualify for tax exemptions if they meet specific conditions related to foreign investment and business activities.
Exploring Corporate Tax-Free Zones in the UAE
The UAE has long been known for its attractive free zones, which offer various incentives to businesses, including exemptions from corporate tax. These zones are designed to foster specific industries such as technology, trade, logistics, and manufacturing, among others.
What Are Corporate Tax-Free Zones?
Corporate tax-free zones are specialized areas in the United Arab Emirates where businesses can enjoy various benefits, including exemptions from corporate tax, customs duties, and other regulatory advantages. These zones are designed to attract foreign investment and promote economic diversification by providing a favorable business environment.
Key Benefits of Corporate Tax-Free Zones
- 0% Corporate Tax
Businesses that meet the necessary criteria in free zones are exempt from corporate tax, sometimes for up to 50 years, depending on the specific free zone. - 100% Foreign Ownership
Unlike mainland companies, foreign investors in free zones can fully own their businesses without the need for a local sponsor or partner. - No Import/Export Duties
Free zone businesses enjoy exemptions from import and export duties, making it easier and more cost-effective to trade internationally. - Simplified Company Setup
Setting up a business in a free zone is typically quicker and more straightforward than in the mainland, as many free zones offer one-stop-shop services that streamline the process. - Full Repatriation of Profits
Companies can repatriate 100% of their profits and capital, providing further financial flexibility for foreign investors. - Exemption from Personal Income Tax
Free zone employees are also exempt from personal income tax, which makes it an attractive option for skilled workers and entrepreneurs.
Types of Free Zones in the UAE
The UAE hosts over 40 free zones, each catering to specific industries. Some of the most prominent ones include:
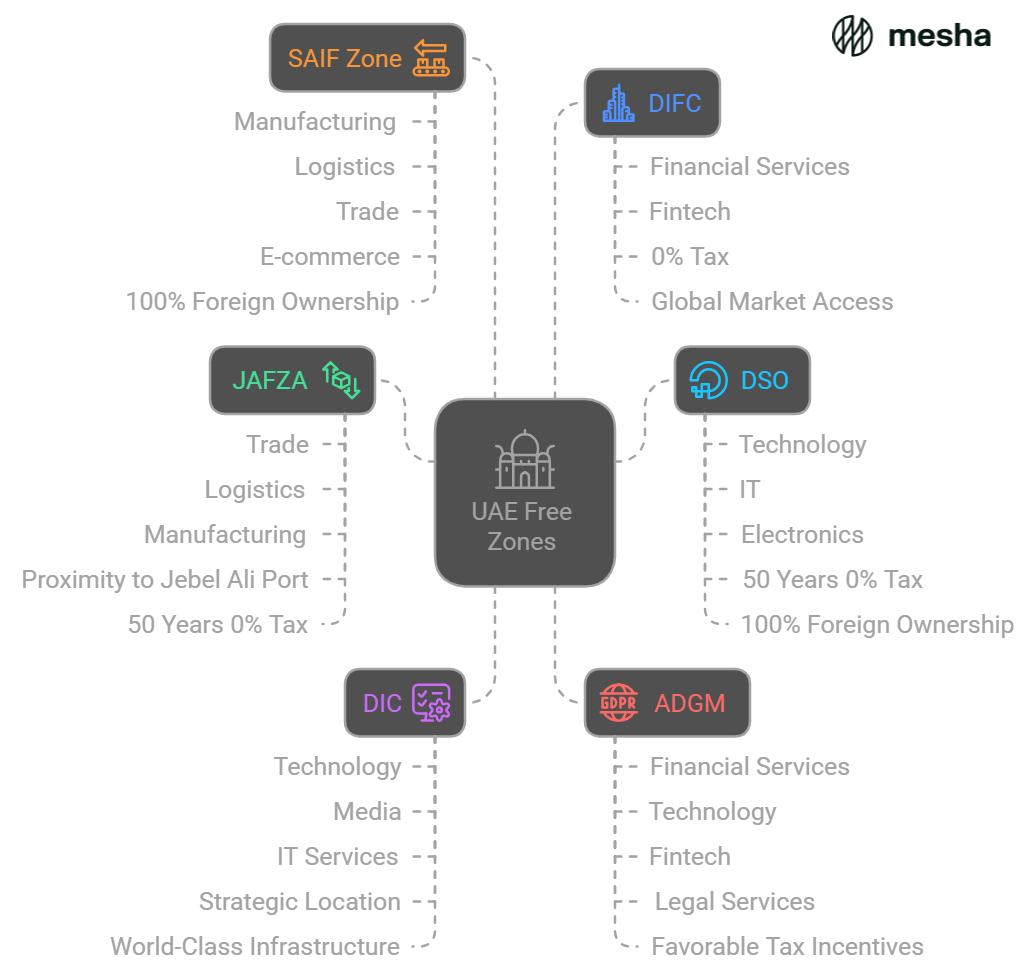
| Free Zone | Industry Focus | Key Features |
| Dubai International Financial Centre (DIFC) | Financial services, fintech | Full legal and regulatory framework, 0% tax, easy access to global markets |
| Jebel Ali Free Zone (JAFZA) | Trade, logistics, manufacturing | Proximity to Jebel Ali Port, 0% corporate tax rate for 50 years |
| Dubai Silicon Oasis (DSO) | Technology, IT, electronics | 0% corporate tax for 50 years, 100% foreign ownership |
| Dubai Internet City (DIC) | Technology, media, and IT services | Strategic location, world-class infrastructure |
| Abu Dhabi Global Market (ADGM) | Financial services, technology, fintech, legal services | Full regulatory system, favorable tax incentives |
| Sharjah Airport International Free Zone (SAIF Zone) | Manufacturing, logistics, trade, e-commerce | 0% corporate tax, 100% foreign ownership |
Free Zone Business Structure and Compliance
To enjoy the benefits of operating within a corporate tax-free zone, businesses must adhere to the rules and regulations of the specific zone. Common requirements include:
- Business Activity Restrictions
Each free zone typically has a designated list of approved activities that businesses must align with. For example, a free zone focusing on logistics may not permit manufacturing businesses. - Physical Presence Requirement
Free zone businesses must have a physical presence within the zone, such as an office or warehouse. The required space varies depending on the zone. - Economic Substance Regulations
Businesses must demonstrate real economic activity within the zone. This includes maintaining a certain number of employees and having a local office to avoid challenges during tax audits.
How to Choose the Right Free Zone
Selecting the right free zone depends on several factors, including:
- Industry Focus
Choose a free zone that caters to your industry. Some zones specialize in technology, while others focus on logistics, manufacturing, or healthcare. - Business Goals
Consider the long-term goals of your business. If you plan to expand globally, free zones with international trade links may be more suitable. - Location
The geographical location of the free zone matters. For example, zones near major ports, such as JAFZA, are ideal for logistics and shipping businesses. - Cost
Setting up and maintaining a business in a free zone comes with specific costs, such as registration fees and office space rental. Be sure to evaluate your budget before committing.
Free Zone vs. Mainland: What’s the Difference?
| Feature | Free Zone | Mainland |
| Ownership | 100% foreign ownership | 51% local ownership required |
| Tax Exemption | 0% corporate tax (up to 50 years) | Standard corporate tax applies (9%) |
| Location | Located in specific areas (not in city centers) | Can operate throughout the country |
| Business Scope | Limited to certain activities within the zone | Can do business with the entire UAE market |
| Setup Time | Faster and simpler process | More complex setup process |
Who Should Consider a Free Zone?
Free zones are best suited for businesses looking to:
- Start-Up Quickly: Free zones are ideal for startups due to their fast setup processes.
- Engage in International Trade: Businesses that deal with international customers can benefit from tax exemptions on imports and exports.
- Need 100% Foreign Ownership: Foreign entrepreneurs or investors who prefer full control over their business operations.
- Operate in Specific Industries: If your business fits within the focus of a specific free zone, you can take advantage of specialized services and infrastructure.
Essential Corporate Tax Forms for UAE Filing
Filing corporate tax returns in the UAE is an important aspect of complying with the Federal Tax Authority (FTA) regulations. Companies are required to submit several forms to ensure they meet their tax obligations correctly.
Corporate Tax Forms Overview
The UAE’s corporate tax filing system requires businesses to submit various forms depending on the type of tax and business structure. These forms help the FTA to assess the business’s tax liability and ensure compliance with the law.
Key Forms for Corporate Tax Filing
- Tax Registration Form (TRN Application)
- Purpose: Used to apply for a Tax Registration Number (TRN), which businesses must obtain before filing tax returns.
- Required Information:
- Business license details
- Company legal name and address
- Contact details for the business
- Type of business activities
- Corporate Tax Return Form (CT1)
- Purpose: The main form for submitting annual corporate tax returns.
- Required Information:
- Financial statements (Balance sheet, Profit & Loss statement)
- Income and expense details for the relevant fiscal year
- Calculation of tax due (if applicable)
- Information about any exemptions or deductions claimed
- Submission Deadline: This form must be submitted within nine months after the end of the company’s financial year.
- Declaration of Exemptions Form
- Purpose: Used to claim exemptions from corporate tax based on specific criteria such as operating in a free zone or qualifying for tax exemptions due to industry-specific rules.
- Required Information:
- Proof of exemption eligibility (e.g., Free Zone Certificate)
- Business activities and relevant income sources
- Financial statements supporting the claim
- Economic Substance Declaration
- Purpose: Required for entities that engage in certain business activities. It confirms that a business is conducting real economic activities in the UAE to meet the FTA’s economic substance requirements.
- Required Information:
- Number of employees and office location
- Details of activities conducted in the UAE
- Financial records showing the business’s physical operations
- Transfer Pricing Documentation
- Purpose: If the business is part of a multinational group, it must submit documentation related to transfer pricing rules. This ensures that intercompany transactions are conducted at arm’s length and are compliant with international tax standards.
- Required Information:
- Details of related-party transactions
- Transfer pricing policies and agreements
- Financial analysis to demonstrate arm’s length pricing
Steps for Filing Corporate Tax Forms
- Register with the FTA
- Before filing any tax returns, ensure that your business is registered with the Federal Tax Authority and has received a valid Tax Registration Number (TRN).
- Prepare Financial Statements
- Prepare the necessary financial statements for the relevant tax year. These include:
- Balance sheet
- Profit and loss statement
- Cash flow statement
- Ensure all transactions and financial activities are accurately recorded.
- Prepare the necessary financial statements for the relevant tax year. These include:
- Fill Out the Required Forms
- Complete the relevant corporate tax forms, including the Corporate Tax Return (CT1) and any other forms related to exemptions or economic substance.
- Ensure all information is accurate and complete.
- Submit the Forms Online
- Log into the FTA portal (www.tax.gov.ae) to submit the forms electronically. The FTA offers an online filing system that allows businesses to submit their forms and track their tax returns.
- Pay Tax Due (If Applicable)
- If the tax return indicates that tax is due, make the payment using the FTA’s secure online payment system. Be mindful of the payment deadlines to avoid late fees and penalties.
- Retain Copies for Record Keeping
- After filing the forms, ensure you retain copies of the submission and related documents for at least five years as required by UAE tax law.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Filing Tax Forms
- Incomplete or Incorrect Information
- Always double-check the forms for accuracy. Mistakes in the details provided, such as incorrect income or expense figures, can lead to fines or a delay in processing.
- Missing Deadlines
- Ensure that forms are submitted on time. Missing deadlines may result in late fees or penalties. It’s advisable to submit forms ahead of time to avoid last-minute issues.
- Failure to Claim Eligible Exemptions
- Many businesses, especially those in free zones, may be eligible for corporate tax exemptions. Failing to claim these exemptions or submitting the incorrect form can lead to unnecessary tax liabilities.
- Not Providing Required Supporting Documents
- Forms like the Economic Substance Declaration or Transfer Pricing Documentation require supporting documents. Ensure these are attached to avoid delays or rejection of your submission.
Key Deadlines for UAE Corporate Tax Returns
Understanding the deadlines for submitting corporate tax returns is crucial for businesses operating in the UAE. Failing to meet these deadlines can result in penalties and legal complications.
Understanding the Tax Year in the UAE
In the UAE, the corporate tax year generally aligns with the fiscal year of the business. However, businesses can opt to have a financial year that does not necessarily coincide with the calendar year, as long as they specify this at the time of registration with the Federal Tax Authority (FTA).
Typically, companies must submit their corporate tax return within nine months from the end of their financial year. For example, if a business’s fiscal year ends on December 31, the corporate tax return would be due by September 30 of the following year.
Key Deadlines for Corporate Tax Filing
- Corporate Tax Return Filing Deadline (CT1 Form)
The main corporate tax return form (CT1) must be submitted within 9 months after the end of the company’s financial year. This means that if your financial year ends on December 31, the deadline for submitting your corporate tax return would be September 30 of the following year.
Example:- Business fiscal year ends: December 31, 2024
- Tax return filing deadline: September 30, 2025
- Economic Substance Declaration Deadline
Businesses that meet the criteria for economic substance requirements must submit an economic substance declaration. This form must be submitted within 6 months from the end of the business’s financial year.
Example:- Business fiscal year ends: December 31, 2024
- Economic substance declaration deadline: June 30, 2025
- Transfer Pricing Documentation Deadline
For companies involved in international trade or part of multinational groups, transfer pricing documentation must be submitted along with the corporate tax return. This must be submitted before the corporate tax return deadline, ensuring businesses meet compliance on intercompany pricing regulations. - VAT Filing Deadlines (if applicable)
If your business is registered for VAT, VAT returns are typically due on a quarterly or bi-monthly basis, depending on your business’s turnover and VAT registration. While VAT is separate from corporate tax, timely VAT filings are equally important to avoid penalties.
Tax Filing Reminder Tips
To help ensure that your business remains compliant, consider implementing the following practices:
- Create a Tax Calendar
Mark key deadlines for tax returns, economic substance declarations, and VAT filings on your business calendar to stay on track throughout the year. - Maintain Regular Financial Records
Keeping accurate and up-to-date financial records throughout the year ensures that you’re prepared when it’s time to file your returns. - Hire a Professional Tax Consultant
Working with a tax advisor or consultant can help ensure that your filings are correct, timely, and comply with UAE tax laws. - Automate Tax Filing Reminders
Use accounting software or tax filing platforms that send automated reminders before the submission deadlines to avoid last-minute rushes.
Special Considerations for Free Zone Businesses
Free zone businesses may have different filing deadlines depending on the nature of their activities and the specific rules of the free zone in which they operate. These businesses are also required to file corporate tax returns, even if they qualify for tax exemptions.
- Free Zone Filing Deadlines
For free zone companies, the deadlines for filing corporate tax returns typically follow the same schedule as mainland companies (i.e., within 9 months of the end of the fiscal year). However, it is important for businesses to confirm the specific rules of their free zone as some zones may have additional forms or requirements. - Exemption Documentation
Companies claiming tax exemptions (e.g., due to their activities being limited to the free zone or qualifying for specific incentives) must ensure they submit the appropriate supporting documents with their tax returns.
How UAE Corporate Tax Affects the Economy
In 2023, the UAE introduced a federal corporate tax rate of 9% for businesses that generate taxable income exceeding AED 375,000. This marked a historic change for a country that had previously operated with no corporate income tax, except for oil companies and foreign banks.
The corporate tax is part of the UAE’s efforts to modernize its tax system, generate non-oil revenues, and comply with global tax norms. However, the introduction of the corporate tax is balanced by several incentives, including exemptions for free zone businesses and provisions for tax optimization.
Impact on Businesses
- New Revenue Streams for the Government
The corporate tax system aims to provide the government with a stable and sustainable source of revenue, reducing its dependency on oil exports. This is crucial for the UAE’s long-term economic stability, particularly as the global energy market continues to evolve. - Incentive for Foreign Investment
The UAE’s tax-free zones, along with the relatively low corporate tax rate of 9%, continue to make it an attractive destination for foreign investment. The predictable tax environment, combined with other benefits such as 100% foreign ownership and repatriation of profits, helps companies maximize their returns. - Encouraging Transparency and Compliance
The introduction of corporate tax increases transparency and encourages businesses to maintain accurate financial records, ensuring a fair and compliant business environment. This move aligns the UAE with international standards for tax reporting and corporate governance. - Administrative Costs for Businesses
Businesses now need to invest in tax compliance, which includes hiring professionals or outsourcing tax services to ensure they meet the new corporate tax filing requirements. This might lead to additional administrative costs for companies, particularly small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).
Impact on Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises (SMEs)
For SMEs, the corporate tax system could present both challenges and opportunities:
- Challenges of Tax Compliance
While SMEs will generally be subject to the same tax rate as larger corporations, smaller businesses may find it difficult to navigate the administrative requirements associated with tax filing. Additionally, businesses with limited resources may face higher costs when seeking professional advice or setting up internal tax departments. - Opportunities for Growth
On the flip side, the introduction of corporate tax ensures a level playing field for SMEs. With large corporations also subject to taxation, SMEs may have a chance to compete more fairly in the market. Furthermore, corporate tax revenue can be reinvested in infrastructure, education, and healthcare, which may benefit SMEs indirectly by improving the business environment. - Free Zone Exemptions
Many SMEs that set up in free zones can still benefit from tax exemptions, making it easier for them to thrive while they scale their businesses. The government’s intention is to support the growth of SMEs by offering incentives for innovation and entrepreneurship in designated zones.
Impact on Key Sectors in the United Arab Emirates Economy
Several sectors of the UAE economy are directly impacted by the new corporate tax, each in different ways:
- Real Estate Sector
The UAE’s real estate sector, which has been a key driver of economic growth, is likely to see moderate changes due to corporate tax. While real estate developers will now face tax obligations, those who operate in free zones or hold long-term assets may benefit from exemptions or preferential tax rates. Additionally, the government may introduce policies to mitigate any negative effects, such as tax deductions for sustainable or green developments. - Technology and Innovation
The UAE is keen to become a hub for innovation and technology. As part of its economic diversification strategy, the government has focused on creating favorable conditions for technology companies. Tech startups in free zones are largely exempt from corporate tax for an extended period, helping them reinvest their profits into growth and innovation. - Financial Services
The financial services sector, particularly in hubs like the Dubai International Financial Centre (DIFC) and Abu Dhabi Global Market (ADGM), continues to benefit from the UAE’s pro-business tax policies. Companies in these sectors can continue to operate with favorable tax rates, including zero tax on profits for certain financial activities, allowing them to remain competitive on the global stage. - Manufacturing and Industrial Sectors
The UAE’s corporate tax system also impacts the manufacturing and industrial sectors, which are part of the government’s efforts to reduce its reliance on oil exports. These sectors can still benefit from tax incentives such as exemptions for investments in certain industries or from operating in free zones. The government’s focus on diversification is expected to drive more investment in manufacturing, which will contribute to long-term economic growth.
Impact on Global Trade and UAE’s Position in the International Market
- Attracting International Businesses
With the implementation of a low corporate tax rate, the UAE is positioning itself as a competitive business hub. The tax rate is still lower than in many other countries, making it an attractive option for multinational corporations looking to expand their operations in the Middle East. The tax system provides a stable and predictable environment for businesses engaged in global trade. - Alignment with Global Tax Standards
The introduction of corporate tax is part of the UAE’s effort to comply with international tax norms, including the OECD’s guidelines on Base Erosion and Profit Shifting (BEPS). This move ensures that the UAE remains compliant with global tax treaties and improves its standing as a financial hub in the Middle East.
Long-Term Economic Outlook
In the long run, corporate tax in the UAE is expected to drive economic diversification, attracting foreign investment, and promoting innovation. While businesses may face initial challenges in adjusting to the new tax framework, the benefits, including reinvestment in public services, infrastructure, and human capital development, are expected to outweigh the costs.
The UAE’s move toward a more diversified revenue model through corporate tax is a crucial step in ensuring sustainable economic growth and reducing dependence on oil. This will pave the way for a more resilient economy that is better equipped to face global economic challenges.
How to Save on Corporate Taxes in UAE
The UAE’s introduction of corporate tax has raised the importance of tax planning for businesses. While the corporate tax rate is relatively low at 9%, companies still need to explore strategies to minimize their tax liability legally. In this guide, we will discuss various methods businesses can use to save on corporate taxes in the UAE.
1. Take Advantage of Free Zone Exemptions
One of the most significant opportunities for businesses to save on corporate taxes in the UAE is by operating within one of the many free zones across the country. Free zones offer a range of benefits, including tax exemptions and incentives designed to attract foreign investors.
- Tax Exemptions: Companies in UAE free zones can be exempt from corporate tax for a specific period, usually 15-50 years, depending on the zone. Some zones also offer exemptions on VAT, import/export duties, and personal income taxes.
- 100% Foreign Ownership: Unlike in the mainland, businesses in free zones can be 100% foreign-owned, without the need for a UAE national partner. This is a huge advantage for international companies looking to establish a presence in the UAE.
- Eligibility for Free Zone Exemptions: To benefit from free zone exemptions, businesses must meet certain criteria, such as engaging in specific types of activities (e.g., trading, consulting, manufacturing) and ensuring they do not engage in business activities outside the free zone.
Example:
A tech company in the Dubai Silicon Oasis (DSO) could enjoy a 100% tax exemption for up to 50 years. This allows the business to reinvest profits into growth without worrying about corporate tax liabilities.
2. Leverage Tax Deductions and Credits
The UAE corporate tax law allows businesses to reduce their taxable income through various deductions and credits. By claiming eligible deductions, businesses can lower their taxable income, thus reducing their overall tax liability.
- Business Expenses: Many business-related expenses, such as operating costs, salaries, office rent, and utility bills, can be deducted from taxable income. These expenses directly contribute to the business’s operation and can significantly reduce tax liability.
- Research and Development (R&D) Costs: Companies that invest in innovation and R&D may qualify for specific tax credits or deductions. The UAE government encourages businesses to invest in technology and innovation by offering tax incentives.
- Depreciation of Assets: Depreciation of assets, such as machinery, equipment, and vehicles, can be deducted over time. This reduces the amount of taxable income, especially for businesses that rely on heavy machinery or capital-intensive assets.
Example:
A manufacturing company that buys new machinery may claim depreciation deductions on the machinery’s value, thereby lowering taxable income and saving on corporate tax.
3. Engage in Transfer Pricing
For businesses operating as part of a multinational group, transfer pricing can be a key strategy to minimize tax liabilities. Transfer pricing refers to the pricing of goods, services, and intellectual property transferred between related companies in different countries.
- Arm’s Length Pricing: The UAE’s corporate tax rules require that transactions between related entities be priced at “arm’s length” – meaning the prices charged should be similar to what would be charged between independent entities. Businesses can use this principle to structure transactions in a way that minimizes their overall tax burden.
- Transfer Pricing Documentation: To comply with international tax regulations, businesses must maintain proper transfer pricing documentation that justifies their pricing strategies. Failure to comply with these rules could result in penalties.
Example:
A UAE-based subsidiary of a multinational company may sell goods to its parent company in a lower-tax jurisdiction. By setting appropriate transfer prices, the company can allocate more profits to the UAE, where the tax rate is lower, and reduce tax exposure in higher-tax jurisdictions.
4. Consider Holding Companies
UAE businesses can set up holding companies to benefit from favorable tax policies. Holding companies are often used to manage investments in subsidiaries and other business ventures.
- Tax Benefits of Holding Companies: A holding company in the UAE may benefit from certain exemptions, such as tax exemptions on dividends and capital gains from investments in other companies. This can result in significant tax savings if the company holds investments in multiple businesses.
- Investment in Real Estate: A holding company can be used to manage real estate investments, potentially offering tax advantages such as deductions for interest payments, property expenses, and depreciation.
Example:
A UAE-based holding company with investments in several international subsidiaries can potentially reduce its taxable income by utilizing tax-efficient structures, such as exempting dividends from tax and optimizing the holding structure for capital gains tax savings.
5. Optimize Employee Compensation and Benefits
Employee compensation packages can also be structured in ways that reduce tax liability. Businesses can provide various forms of compensation that may not be subject to corporate tax, such as:
- Bonuses and Profit Sharing: Structuring employee compensation as performance-based bonuses or profit-sharing schemes can provide tax-efficient ways to pay employees, as these may be deductible expenses for the company.
- Non-Cash Benefits: Instead of cash bonuses, companies can offer non-cash benefits such as healthcare, transportation, or education allowances. These benefits may be deductible for the business and not subject to tax.
Example:
Instead of paying high cash salaries, a business could offer employees housing allowances or travel stipends, which can reduce the overall taxable income of the company.
6. Explore Double Taxation Agreements (DTAs)
The UAE has signed Double Taxation Agreements (DTAs) with numerous countries to help avoid the double taxation of income. DTAs ensure that businesses are not taxed twice on the same income – once in the country where the income is earned and again in the UAE.
- Reduced Withholding Tax: DTAs often include provisions that reduce or eliminate withholding tax on cross-border payments such as dividends, royalties, and interest.
- Tax Credits for Foreign Taxes Paid: If a business pays taxes in a foreign jurisdiction, it may be able to claim a credit against its UAE tax liability, reducing the amount of tax owed in the UAE.
Example:
A UAE-based company earning income from a European subsidiary may be able to claim a reduced withholding tax rate on royalties or dividends, thanks to a DTA between the UAE and the relevant European country.
7. Reinvest Profits for Tax Optimization
Reinvesting profits into the business is one of the simplest ways to reduce taxable income. The UAE tax system allows businesses to reinvest profits into expansion, R&D, or other capital expenditures without facing immediate tax implications.
- Reinvestment in Assets: Purchasing new equipment, technology, or expanding operations can reduce taxable income by increasing allowable deductions.
- Investing in Innovation: Businesses can reinvest profits in research, product development, and innovation, which may qualify for tax credits or deductions, further reducing their overall tax burden.
Example:
A company that reinvests profits into developing a new product line or opening a new branch may qualify for deductions related to those investments, reducing their taxable income.
Corporate Tax Penalties in the UAE: Avoid Costly Mistakes
The UAE has a strict framework for ensuring compliance with corporate tax laws. Under the Federal Tax Authority (FTA), businesses are required to file their corporate tax returns on time, pay taxes owed, and maintain accurate financial records. Failure to meet these requirements can result in substantial penalties.
The penalties can be imposed for various reasons, including late filings, incorrect filings, failure to pay taxes, and non-compliance with other tax regulations. The goal of these penalties is to encourage businesses to adhere to tax laws and promote transparency and fairness within the tax system.
Types of Penalties Businesses Can Face
- Late Filing Penalties
One of the most common penalties businesses face is the fine for late submission of corporate tax returns. Companies are required to file their tax returns within 9 months after the end of their financial year. If they miss this deadline, they will be subject to penalties.
| Violation | Penalty |
| Late submission of corporate tax return | AED 10,000 for the first offense, AED 20,000 for subsequent offenses |
- Failure to Pay Taxes on Time
If a business fails to pay its corporate tax on time, it will incur penalties in addition to the unpaid tax. The UAE tax system requires that taxes be paid within the filing deadline.
| Violation | Penalty |
| Failure to pay taxes on time | Interest of 1% per month on the outstanding tax amount |
| Plus an additional 4% penalty if payment is delayed by more than 20 days |
- Inaccurate or Incorrect Filings
Submitting inaccurate or incomplete corporate tax returns can lead to hefty penalties. If the FTA determines that a business has intentionally underreported its income or inflated its expenses, this can lead to criminal charges, fines, and potentially even the suspension of operations.
| Violation | Penalty |
| Inaccurate or false tax returns | Fines up to AED 50,000, or higher, depending on the severity of the violation |
- Failure to Maintain Adequate Financial Records
Businesses are required to maintain proper accounting records to support their corporate tax filings. Failing to maintain accurate records can lead to penalties and additional scrutiny from tax authorities.
| Violation | Penalty |
| Failure to maintain adequate financial records | AED 10,000 for the first offense, AED 20,000 for subsequent offenses |
- Failure to Submit Economic Substance Declaration
Companies that fall under the Economic Substance Regulations must submit an economic substance declaration along with their corporate tax returns. If a company fails to meet this requirement, they could face penalties.
| Violation | Penalty |
| Failure to submit economic substance declaration | AED 20,000 for the first year, AED 50,000 for subsequent years |
How to Avoid Corporate Tax Penalties in the UAE
- Stay Organized and Maintain Proper Records
One of the most effective ways to avoid penalties is by maintaining accurate and up-to-date financial records. This includes keeping detailed accounts of all income, expenses, assets, and liabilities. Proper record-keeping ensures that businesses are ready for any tax audits and can submit accurate tax returns.
- Tip: Use accounting software or hire a professional accountant to ensure your records are comprehensive and comply with tax laws.
- File Corporate Tax Returns on Time
Timely filing of tax returns is crucial to avoid late submission penalties. Remember, businesses must file their tax returns within 9 months of the end of their fiscal year. Set reminders in advance to ensure that all forms are submitted on time.
- Tip: Create a tax calendar with all key deadlines and automate reminders to avoid missing the filing dates.
- Ensure Accuracy in Your Tax Returns
Double-check all figures and calculations when preparing your corporate tax return. Inaccurate reporting can lead to fines or more severe penalties. If you’re unsure about any figures or deductions, consult with a tax advisor.
- Tip: Seek professional help or hire a tax consultant if you have doubts about your tax calculations or filings.
- Pay Taxes Promptly
Ensure that your business pays any corporate tax liabilities on time. Late payments can lead to interest charges, and if payments are delayed for more than 20 days, additional penalties will apply.
- Tip: Set up automated payments or establish a dedicated tax account to ensure taxes are paid on time.
- Stay Updated on Tax Laws and Regulations
The UAE’s tax regulations are evolving, and it’s crucial for businesses to stay informed about any changes to corporate tax laws. This includes understanding any new exemptions, deductions, or amendments to filing procedures.
- Tip: Subscribe to updates from the UAE Federal Tax Authority or work with a tax advisor to stay on top of regulatory changes.
- Submit Economic Substance Declarations on Time
Companies that are subject to the Economic Substance Regulations must submit the required economic substance declaration. Failing to do so will result in penalties.
- Tip: Review whether your business activities fall under these regulations and ensure timely submission of the required forms.
What to Do If You Receive a Penalty
If your business receives a penalty, it’s essential to act quickly:
- Review the Notice: Carefully review the penalty notice from the FTA to understand why the penalty was imposed.
- File an Appeal: If you believe the penalty was issued in error, you have the right to appeal. The FTA allows businesses to challenge penalties within a specific time frame.
- Pay the Penalty: If the penalty is valid, make sure to pay it promptly to avoid additional charges or further enforcement actions.
- Implement Preventative Measures: To avoid future penalties, consider revising your tax practices and ensuring that all filings and payments are made correctly and on time.
Corporate Tax Audits: What to Expect
A corporate tax audit is an examination of a company’s financial records and transactions by the UAE’s Federal Tax Authority (FTA). The goal of the audit is to ensure that businesses are complying with corporate tax laws, including filing tax returns accurately, paying the correct amount of tax, and maintaining the necessary documentation.
The FTA has the authority to audit any company subject to corporate tax, and audits can be triggered for various reasons, such as random selection, discrepancies in tax filings, or suspicious activities. The FTA’s main aim is to ensure that businesses are paying their fair share of taxes and adhering to tax regulations.
Reasons for a Corporate Tax Audit
While tax audits in the UAE are not always anticipated, there are several reasons why a business might be selected for an audit. These include:
- Discrepancies in Tax Filings: If the information on a company’s tax returns doesn’t align with their financial records or previous filings, it can raise red flags. This could include underreporting income, overreporting expenses, or claiming ineligible deductions.
- Failure to File Returns on Time: Companies that have a history of late filings or non-compliance with tax deadlines may be subject to an audit. Late payments of taxes or inconsistent tax filings can signal that a business might not be adhering to proper tax regulations.
- Random Selection: Just like in many other jurisdictions, businesses can be selected for an audit randomly. This is part of the FTA’s strategy to ensure all businesses are complying with tax regulations.
- Suspicious Transactions or Patterns: If a business engages in transactions that appear unusual or suspicious—such as large transfers or complex financial arrangements—the FTA may initiate an audit to investigate further.
- Economic Substance Violations: Businesses that are required to adhere to the Economic Substance Regulations may be audited to ensure they meet the requirements for economic substance. Failing to meet these regulations can lead to penalties, including the imposition of fines.
What Happens During a Corporate Tax Audit?
A corporate tax audit typically involves the FTA reviewing your business’s financial records and tax filings. Below is an overview of what to expect during the audit process:
- Notification of the Audit: The FTA will notify the company in writing that an audit is being conducted. This notification will include the reason for the audit, the scope, and the period under review. In some cases, the audit may focus on a specific issue, while in others, it may cover the entire tax history of the company.
- Document Review: During the audit, the FTA will examine a company’s accounting records, tax filings, financial statements, and any supporting documents such as invoices, contracts, receipts, and bank statements. The FTA may also review the company’s corporate structure, related-party transactions, and transfer pricing arrangements.
- Interviews and Clarifications: The FTA may request interviews or meetings with the company’s management, accountants, or tax advisors to clarify specific transactions or financial practices. It’s essential to be cooperative and transparent during this process.
- Assessment of Tax Liabilities: If the FTA finds any discrepancies or areas of non-compliance during the audit, they will assess additional taxes, penalties, and interest charges. Businesses may also be required to correct their filings and pay the outstanding tax amounts.
- Audit Report and Conclusion: After the audit is completed, the FTA will issue a report detailing the findings, including any tax discrepancies, errors, or violations discovered. The company will have the opportunity to review the report and discuss any disagreements with the FTA.
Potential Outcomes of a Corporate Tax Audit
There are several potential outcomes after a corporate tax audit, depending on the findings:
- No Changes or Penalties: If the audit finds that the company has complied with tax laws and regulations, the audit will close without any changes. This outcome is the best-case scenario for businesses.
- Additional Taxes Owed: If the FTA identifies underreported income or ineligible deductions, the company may be required to pay additional taxes, along with any penalties or interest charges for late payments.
- Penalties for Non-Compliance: If the audit uncovers significant violations, such as deliberate underreporting of income or tax evasion, the company could face penalties. Penalties for serious non-compliance can range from fines to criminal charges, depending on the severity of the violation.
- Tax Adjustments: In some cases, the FTA may adjust a company’s tax filings to ensure that the taxes owed are correct. This could include recalculating income, deductions, or tax credits based on the audit findings.
How to Prepare for a Corporate Tax Audit
Being proactive and prepared for a corporate tax audit can help businesses avoid complications and penalties. Here are a few steps to ensure a smooth audit process:
- Maintain Accurate and Organized Records: Keeping detailed and up-to-date financial records is the first line of defense against an audit. Make sure all transactions are well-documented, and keep all supporting documents such as receipts, contracts, and invoices.
- Understand Tax Filing Requirements: Ensure that your company fully understands and complies with UAE tax filing requirements. This includes adhering to deadlines, correctly reporting income and expenses, and understanding tax laws relevant to your business.
- Consult with Tax Experts: If your company faces a complex audit, it’s advisable to consult with tax professionals or advisors who are well-versed in UAE tax laws. They can help you navigate the audit process, respond to FTA inquiries, and represent your company during any discussions or negotiations.
- Perform Internal Audits: Conduct regular internal audits to ensure your records and tax filings are accurate. An internal audit can help you identify potential issues before the FTA comes to review your tax returns.
- Respond Promptly to Audit Requests: If the FTA requests specific documents or clarifications, respond promptly and provide the necessary information. Cooperation can lead to a more favorable outcome.
What to Do If Your Business is Audited
If your business is selected for a tax audit, here are some important steps to follow:
- Review the Audit Notice: Carefully read the audit notice to understand the scope and nature of the audit. This will help you prepare the necessary documents.
- Gather Required Documentation: Collect all the requested financial records and tax filings. Be prepared to provide any supporting documents that may be needed, including bank statements, invoices, and contracts.
- Consult with Experts: Engage a tax consultant or legal advisor to guide you through the audit process. They can help you prepare for meetings, ensure compliance with tax laws, and represent your business if disputes arise.
- Address Any Issues Found: If the audit uncovers any discrepancies or errors, work with the FTA to resolve the issues as soon as possible. This could involve correcting filings, paying additional taxes, or addressing any compliance failures.
Key Corporate Tax Treaties in the UAE
A corporate tax treaty is an agreement between two countries that aims to avoid double taxation on income earned by a company operating in both jurisdictions. These treaties are essential for businesses that operate internationally, as they help determine which country has taxing rights over various types of income, such as dividends, interest, royalties, and business profits.
The main objectives of corporate tax treaties include:
- Eliminating Double Taxation: Treaties ensure that businesses are not taxed twice on the same income—once in the country where the income is generated and again in the country of residence of the business.
- Reducing Tax Rates: Tax treaties often provide reduced withholding tax rates on dividends, interest, and royalties, which can lower the overall tax burden for companies operating internationally.
- Providing Tax Certainty: Tax treaties help provide clarity on tax obligations, reducing the risk of disputes between businesses and tax authorities.
UAE’s Network of Tax Treaties
As part of its efforts to integrate into the global economy and attract international investors, the UAE has signed numerous tax treaties with other countries. The UAE has a network of over 130 double tax treaties (DTTs) with countries across the globe. These treaties cover a wide range of tax matters and help reduce the burden of taxation on businesses and investors.
The UAE’s tax treaty network includes agreements with major economies such as:
- United Kingdom
- United States
- India
- China
- Germany
- France
- Japan
- Singapore
- Saudi Arabia
These treaties are important for businesses in the UAE, as they provide various tax advantages for companies doing business internationally.
Benefits of Corporate Tax Treaties for UAE Businesses
- Avoidance of Double Taxation
One of the primary benefits of corporate tax treaties is the prevention of double taxation. Without a tax treaty, a company that earns income in another country may be taxed by both that country and the UAE, resulting in double taxation. A tax treaty allocates taxing rights between the two countries, ensuring that businesses are only taxed once on income generated abroad.
For example, if a UAE-based company receives dividends from a subsidiary in the United Kingdom, the income may be subject to withholding tax in the UK. However, under the UAE-UK tax treaty, the UAE business may be eligible for a reduced withholding tax rate, or even a complete exemption from UK tax on dividends.
- Reduced Withholding Tax Rates
Corporate tax treaties often reduce or eliminate withholding taxes on income such as dividends, interest, and royalties. This can result in significant tax savings for companies engaged in cross-border transactions.
| Income Type | Typical Tax Rate without Treaty | Typical Tax Rate under UAE Treaty |
| Dividends | 10% – 30% | 5% – 10% |
| Interest | 15% | 5% – 10% |
| Royalties | 15% | 5% – 10% |
These reduced tax rates can significantly lower the overall cost of doing business and increase profitability for UAE-based companies with international operations.
- Clarity and Certainty
Tax treaties provide clear guidelines on which country has the right to tax certain types of income. This reduces the risk of tax disputes between businesses and tax authorities and offers a level of tax certainty for companies operating internationally.
- Tax Relief for Expatriates and Foreign Investors
Corporate tax treaties can also benefit expatriates and foreign investors working in the UAE. Many treaties contain provisions that help expatriates avoid double taxation on income earned both in their home country and in the UAE. Additionally, tax treaties often reduce the tax burden on foreign investors by offering exemptions or reductions on capital gains tax.
Notable UAE Corporate Tax Treaties
Let’s take a closer look at some of the most important corporate tax treaties that the UAE has signed with other countries:
UAE-United States Tax Treaty
The UAE and the United States signed a double tax treaty (DTT) to avoid double taxation and to facilitate trade and investment between the two countries. Key benefits of the UAE-US treaty include:
- Exemption of Dividends: Dividends paid by a UAE company to a US investor are typically exempt from UAE withholding tax, and the tax rate on dividends in the US is reduced under the treaty.
- Reduced Withholding Taxes on Royalties: The treaty provides a reduced withholding tax rate on royalties paid to US companies.
- Tax Credits for US Residents: US residents who pay tax in the UAE can often claim tax credits to offset US tax liabilities.
UAE-India Tax Treaty
The UAE and India have a comprehensive tax treaty that covers various aspects of taxation, including income tax, business profits, and capital gains. Key benefits of the UAE-India treaty include:
- Lower Withholding Taxes: The treaty reduces the withholding tax on dividends, interest, and royalties, benefiting businesses engaged in cross-border transactions between the two countries.
- Exemption from Capital Gains Tax: The treaty ensures that UAE-based companies are not subject to capital gains tax when selling shares in Indian companies, provided certain conditions are met.
- Tax Residency Benefits: The treaty includes provisions that help determine tax residency, preventing both India and the UAE from taxing the same income.
UAE-Singapore Tax Treaty
Singapore and the UAE have a tax treaty that offers several tax benefits to businesses. These benefits include:
- Exemption on Dividends: Dividends paid between Singapore and UAE companies are generally exempt from withholding tax under the treaty.
- Reduced Rates on Interest and Royalties: The treaty reduces withholding tax rates on interest and royalties between the two countries, which is particularly beneficial for businesses in the finance, technology, and intellectual property sectors.
How to Utilize Tax Treaties Effectively
- Understand Treaty Provisions
Companies should thoroughly review the provisions of the relevant tax treaties to understand the benefits available to them. This includes understanding the withholding tax rates, exemptions, and any other tax relief available under the treaties.
- Keep Accurate Records
To benefit from tax treaty provisions, businesses must maintain accurate and up-to-date records of their transactions with foreign entities. This includes keeping track of income earned, tax paid, and any required forms or certificates related to the treaty benefits.
- Consult with Tax Experts
Navigating the complexities of international tax treaties can be challenging. It’s advisable for businesses to consult with tax advisors or consultants who specialize in UAE tax law and international tax treaties. These professionals can help ensure that businesses are maximizing the benefits available under tax treaties and complying with all relevant regulations.
Key Corporate Tax Treaties in the UAE
The UAE has established itself as a global business hub, thanks in part to its extensive network of Double Taxation Avoidance Agreements (DTAs) and other corporate tax treaties. These agreements aim to eliminate double taxation, foster international trade, and attract foreign investment.
What are Corporate Tax Treaties?
Corporate tax treaties are agreements between two countries to reduce or eliminate taxation on income earned across borders. They:
- Prevent double taxation on profits.
- Provide tax relief for companies operating internationally.
- Encourage global business activities.
Overview of UAE’s Tax Treaties
As of 2024, the UAE has signed DTAs with 137 countries, including major trading partners like:
- India
- United States
- United Kingdom
- Germany
- China
How Businesses Can Leverage UAE Tax Treaties
- Choose the Right Entity Type: Multinational companies can optimize taxes by selecting UAE-based entities like Free Zone companies or mainland LLCs.
- Use Treaty Benefits for Expansion: Businesses expanding to treaty countries can negotiate better terms using reduced tax rates.
- Plan Tax Residency Strategically: Maintaining UAE tax residency ensures full access to treaty benefits.
Corporate Tax Registration Requirements in UAE
In the UAE, businesses need to understand the mandatory registration requirements to comply with the country’s tax regulations. Registration is crucial to avoid penalties and maintain smooth operations.
Who Needs to Register for Corporate Tax in UAE?
All businesses operating in the UAE are generally required to register for corporate tax, except those explicitly exempted. Here’s a breakdown:
| Category | Registration Requirement |
| UAE Mainland Companies | Must register, regardless of size or sector. |
| Free Zone Companies | Must register, even if benefiting from a 0% tax rate. |
| Government and Government-Owned Entities | Exempt, unless involved in commercial activities. |
| Small Businesses (Below AED 375,000 Turnover) | Must register but can qualify for a 0% tax rate. |
| Natural Resource Extraction Companies | Exempt under certain conditions. |
Documents Required for Corporate Tax Registration
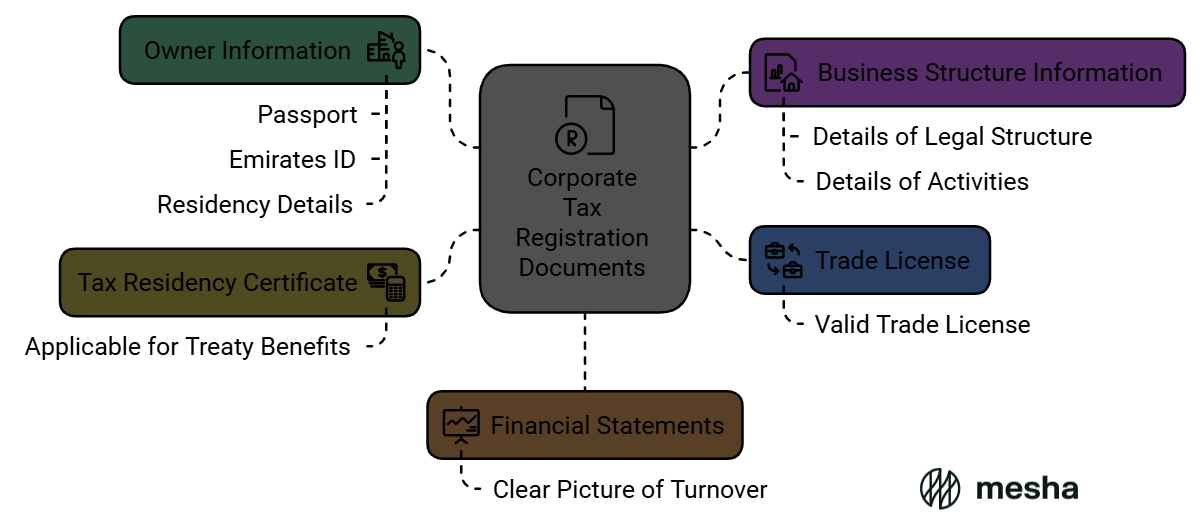
To register successfully, businesses must prepare the following documents:
- Trade License: A copy of the valid trade license.
- Owner Information: Passport, Emirates ID, and residency details for all shareholders or partners.
- Tax Residency Certificate (if applicable): For businesses claiming treaty benefits.
- Financial Statements: For a clear picture of the company’s turnover.
- Business Structure Information: Details of legal structure and activities.
Registration Timeline
Corporate tax registration must be completed well before the first corporate tax filing deadline. Early registration ensures compliance and avoids unnecessary penalties.
Steps to Register for Corporate Tax in UAE
- Create an Account:
Visit the Federal Tax Authority (FTA) website and create a user account. - Provide Business Details:
Enter company details, including trade license number, legal structure, and address. - Upload Documents:
Submit all required documents in digital format. - Verify Information:
Cross-check the details before submitting the application to avoid delays. - Receive Tax Registration Number (TRN):
Once approved, the FTA will issue a unique TRN, confirming your registration.
Exemptions from Registration
Certain entities may be exempt from registering for corporate tax:
- Businesses engaged in natural resource extraction (subject to emirate-level taxation).
- Entities operating within qualifying Free Zones under specific conditions.
Potential Penalties for Non-Compliance
Failing to register for corporate tax can lead to financial and legal repercussions, such as:
- Fines starting from AED 10,000 for non-registration.
- Additional penalties for non-payment or late filing.
Pro-Tip for Businesses
Even if your business qualifies for a 0% corporate tax rate, you are still obligated to register. Keeping proper financial records is essential for future audits or inquiries.
Step-by-Step Guide to Corporate Tax Registration in UAE
Registering for corporate tax in the UAE is a straightforward process when approached systematically. This guide will help businesses navigate each step of the process to ensure compliance with the Federal Tax Authority (FTA) requirements.
Why is Corporate Tax Registration Important?
Corporate tax registration is mandatory for businesses to:
- Fulfill UAE tax law obligations.
- Obtain a Tax Registration Number (TRN) for filing returns.
- Avoid penalties for non-compliance.
Step-by-Step Guide to Register for Corporate Tax
- Prepare the Required Documents
Before beginning the registration process, gather all the necessary documentation:- Trade License: To verify business activities.
- Owner Information: Passport and Emirates ID for all shareholders or partners.
- Business Structure Details: Legal form, address, and ownership details.
- Financial Records: Proof of turnover to determine eligibility for exemptions or reduced rates.
- Create an Account on the FTA Portal
- Visit the Federal Tax Authority’s website.
- Click on “Sign Up” to create an account.
- Provide your email, create a secure password, and verify your account.
- Log In and Access the Corporate Tax Registration Form
- After logging in, navigate to the “Corporate Tax” section on the dashboard.
- Select “Register for Corporate Tax” to access the form.
- Complete the Registration Form
- Business Information: Include trade license number, legal structure, and business type (mainland, free zone, etc.).
- Contact Information: Provide accurate details for communication purposes.
- Owner Details: Enter shareholder or partner information as required.
- Upload Supporting Documents
- Use the upload feature to submit the scanned copies of your trade license, financial records, and ownership documents.
- Review and Submit
- Double-check all entries to ensure accuracy.
- Submit the application and wait for confirmation from the FTA.
- Receive the Tax Registration Number (TRN)
- Upon approval, the FTA will issue a TRN, which serves as your corporate tax identifier.
Example: Corporate Tax Registration Timeline
| Step | Timeline |
| Document Preparation | 1-3 business days |
| Account Creation on FTA Portal | Immediate |
| Form Submission | 1-2 hours |
| FTA Approval and TRN Issuance | 5-10 business days |
What Happens After Registration?
Once registered, businesses must:
- Keep the TRN handy for filing corporate tax returns.
- Maintain accurate financial records for audits.
- Stay updated on tax filing deadlines to avoid penalties.
Step-by-Step Guide to Filing Corporate Tax in UAE
Filing corporate tax returns is an essential requirement for businesses in the UAE to ensure compliance with the Federal Tax Authority (FTA). Understanding the process and timeline can help businesses avoid penalties and focus on their operations.
What is Corporate Tax Filing?
Corporate tax filing involves submitting a formal declaration of a company’s taxable income, applicable deductions, and tax liabilities to the FTA. This must be done annually, even if the business qualifies for a 0% tax rate.
Step-by-Step Guide to Filing Corporate Tax
- Determine Your Financial Year
- Identify your taxable period. Typically, this aligns with the Gregorian calendar (January 1 to December 31), but some businesses may have an alternative fiscal year.
- Ensure your financial statements are prepared for the chosen period.
- Prepare Your Financial Records
- Revenue and Expenses: Compile detailed records of income and expenses.
- Deductions: Identify deductible expenses such as operational costs, salaries, and depreciation.
- Exempt Income: Separate income exempt from corporate tax (e.g., qualifying dividends or Free Zone income).
- Access the FTA Portal
- Visit the Federal Tax Authority’s website.
- Log in using your Tax Registration Number (TRN) and credentials.
- Complete the Tax Return Form
- Navigate to the “Corporate Tax” section and select “File Tax Return.”
- Enter the following details:
- Gross Income: Report all income streams.
- Deductions: Include deductible expenses.
- Taxable Income: Calculate this by subtracting deductions from gross income.
- Applicable Tax Rate: Apply the corporate tax rate (e.g., 9% for most businesses, 0% for qualifying Free Zone entities).
- Upload Supporting Documents
- Attach audited financial statements and other required documents, such as balance sheets and profit-and-loss statements.
- Review and Submit
- Double-check all data for accuracy.
- Submit the tax return and note the confirmation number provided by the portal.
- Pay the Tax Due
- Calculate your tax liability based on the declared taxable income.
- Use the FTA portal to pay the tax due before the deadline.
Example: Tax Filing Workflow
| Step | Estimated Time |
| Preparing Financial Records | 2-3 weeks |
| Completing the Tax Return | 1-2 hours |
| FTA Review and Approval | 5-10 business days |
Corporate Tax Filing Deadlines in UAE
Corporate tax filing deadlines in the UAE are a critical aspect of compliance for businesses. Missing these deadlines can lead to penalties and disrupt operations, making it essential for companies to stay informed and prepared.
General Corporate Tax Filing Deadline
The UAE requires businesses to file their corporate tax returns within 9 months from the end of their financial year. This applies to all taxable entities unless specific exemptions or extensions are provided by the Federal Tax Authority (FTA).
| Financial Year-End Date | Filing Deadline |
| December 31, 2024 | September 30, 2025 |
| March 31, 2025 | December 31, 2025 |
| June 30, 2025 | March 31, 2026 |
| September 30, 2025 | June 30, 2026 |
Key Milestones for Corporate Tax Compliance
- End of Financial Year:
- Align your tax filings with your financial year, typically January to December unless a different fiscal year is approved.
- Preparation of Financial Statements:
- Compile audited financial statements well before the filing deadline to ensure accuracy.
- Filing the Corporate Tax Return:
- Submit the tax return using the FTA portal before the 9-month deadline.
- Payment of Tax Liability:
- Pay any tax due on or before the filing deadline to avoid penalties.
What Happens if You Miss the Deadline?
Failing to meet the corporate tax filing deadlines can result in:
- Late Filing Penalties: Starting at AED 1,000 and escalating with continued non-compliance.
- Interest on Unpaid Taxes: Additional charges on overdue tax liabilities.
- Audit Risks: Increased likelihood of FTA scrutiny for non-compliant businesses.
Strategies to Stay Compliant
- Maintain a Compliance Calendar
- Use digital tools or set reminders to track filing deadlines.
- Engage a Tax Consultant
- Professional advisors can help ensure timely filing and accurate calculations.
- Early Submission
- File your returns early to avoid last-minute technical issues or delays.
- Regular Record Keeping
- Ensure all transactions are properly documented to simplify the tax filing process.
Essential Corporate Tax Forms for UAE Filing
Filing corporate tax returns in the UAE requires the use of specific forms and documentation prescribed by the Federal Tax Authority (FTA). Knowing the required forms and their purposes ensures accurate submissions and compliance with tax regulations.
Key Corporate Tax Forms in UAE
- Corporate Tax Return (Form CT01)
- Purpose: Used to declare taxable income, deductions, and tax liabilities.
- Who Must File: All businesses registered for corporate tax, including those in Free Zones with a 0% tax rate.
- Contents:
- Business income and deductions.
- Taxable income and applicable tax rate.
- Supporting documents for exemptions and deductions.
- Tax Payment Form
- Purpose: For businesses to remit their tax liabilities to the FTA.
- Who Must File: Companies with payable taxes after determining their taxable income.
- Details Required:
- Tax Registration Number (TRN).
- Payment amount and method.
- Tax Refund Request Form
- Purpose: Used to claim refunds for overpaid taxes.
- Who Can Apply: Eligible businesses, including those with excess credits after adjustments.
- Documents Required:
- Proof of overpayment.
- Bank account details for the refund.
- Amendment Request Form
- Purpose: To correct errors or update information in previously submitted returns.
- Who Can File: Businesses identifying inaccuracies in their submissions.
- Details Needed:
- Original return reference number.
- Corrected information with explanations.
Supporting Documents for Filing
| Document | Purpose |
| Audited Financial Statements | Provides accuracy in reported taxable income. |
| Trade License | Validates business operations and legal status. |
| Proof of Deductions | Supports claims for deductible expenses. |
| Income Statements | Details revenue and other income sources. |
| Tax Residency Certificates (if any) | For claiming exemptions under double-taxation treaties. |
Corporate Tax Exemptions in the UAE: Who Qualifies?
The UAE’s corporate tax framework provides several exemptions to support specific industries, activities, and business structures. Understanding who qualifies for these exemptions can help businesses reduce their tax liabilities and optimize their financial planning.
Who Qualifies for Corporate Tax Exemptions in the UAE?
- Free Zone Entities (Qualifying Businesses)
- Businesses operating in designated Free Zones may enjoy a 0% corporate tax rate, provided they meet specific criteria.
- Conditions for Exemption:
- Maintain economic substance in the UAE.
- Generate qualifying income, such as export-driven revenue.
- Avoid conducting business with mainland UAE entities unless otherwise permitted.
- Government-Owned Entities
- Entities wholly owned by the UAE government that conduct mandated activities are exempt from corporate tax.
- Examples: Infrastructure development, public transportation, and healthcare projects under government contracts.
- Non-Profit Organizations
- Charitable institutions, public benefit entities, and other non-profits are exempt if registered and approved by the relevant authorities.
- Eligible Activities:
- Charitable donations and grants.
- Public welfare and community support programs.
- Income from Natural Resources
- Businesses involved in extraction and exploitation of natural resources (oil, gas, minerals) are exempt from federal corporate tax but may still be subject to emirate-level taxation.
- Reason: These industries are regulated under separate laws.
- Income Earned by Individuals
- Personal income earned by individuals, such as salaries, investment returns, and real estate rental income (outside of business activities), is not subject to corporate tax.
Activities That May Qualify for Partial Exemptions
- Investment Income: Dividends and capital gains from domestic or foreign investments may be exempt.
- Intra-Group Transactions: Income from qualifying transactions within a corporate group may also qualify for relief to avoid double taxation.
Steps to Claim Corporate Tax Exemptions
- Determine Eligibility
- Review the FTA’s guidelines for your industry or business structure.
- Register for Corporate Tax
- Even exempt businesses must register with the FTA to confirm their status.
- Maintain Documentation
- Provide evidence such as audited financial statements, Free Zone licenses, or government approvals to support exemption claims.
- Submit Reports
- File annual tax returns to declare your exempt status and report relevant income.
Exploring Corporate Tax-Free Zones in the UAE
The UAE’s Free Zones are economic hubs that attract businesses with their unique tax incentives and regulatory advantages. These zones are pivotal to the UAE’s economy, offering a 0% corporate tax rate for qualifying businesses. Each Free Zone caters to specific industries and operates under its own set of rules.
Key Features of Tax-Free Zones
- 0% Corporate Tax:
- Applies to qualifying income generated within the Free Zone.
- Full Ownership:
- Foreign investors can own 100% of their businesses without requiring a local sponsor.
- Customs Duty Exemptions:
- No duties on imports and exports within the Free Zone.
- Industry-Specific Focus:
- Many Free Zones cater to specific sectors, such as technology, logistics, or media.
- Simplified Business Setup:
- Streamlined registration and licensing processes.
Qualifying for 0% Corporate Tax in Free Zones
To benefit from the 0% corporate tax rate, businesses must:
- Generate Qualifying Income:
- Revenue from outside the UAE or from Free Zone to Free Zone transactions qualifies.
- Income from mainland UAE may not qualify unless permitted.
- Meet Economic Substance Requirements:
- Maintain adequate physical assets, employees, and management in the Free Zone.
- File Annual Tax Returns:
- Even at a 0% tax rate, Free Zone entities must submit returns to the Federal Tax Authority (FTA).
- Avoid Non-Compliant Activities:
- Engaging in prohibited business activities can revoke the tax-free status.
Compliance Challenges for Free Zone Businesses
| Challenge | Resolution |
| Defining Qualifying Income | Clarify with the FTA or seek professional advice. |
| Mainland UAE Transactions | Maintain separate accounting for such income. |
| Economic Substance Compliance | Ensure physical operations meet regulatory standards. |
Advantages of Operating in Free Zones
- Cost Savings:
- Tax exemptions reduce operational costs.
- Ease of Expansion:
- Free Zones provide a global hub for trade and investment.
- Tailored Infrastructure:
- Sector-specific zones offer facilities like warehouses, studios, or tech labs.
- Supportive Ecosystem:
- Free Zones often provide networking opportunities, accelerators, and funding programs.
Limitations of Free Zone Status
- Limited Mainland Access:
- Businesses in Free Zones require local agents for mainland activities.
- Regulatory Differences:
- Each Free Zone has its own rules, which may complicate operations across multiple zones.
How Corporate Tax Affects SMEs in UAE
Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) form the backbone of the UAE economy, contributing significantly to its GDP and employment. The introduction of corporate tax has raised questions about how SMEs will be impacted, given their unique challenges and growth aspirations.
Key Corporate Tax Features Relevant to SMEs
- Corporate Tax Rate:
- SMEs earning less than AED 375,000 annually are taxed at 0%, ensuring smaller businesses are not burdened.
- Income exceeding AED 375,000 is subject to a standard 9% tax rate.
- Exemptions for Free Zone SMEs:
- SMEs operating in designated Free Zones may qualify for a 0% tax rate on specific income streams, provided they meet compliance requirements.
- Compliance Requirements:
- All SMEs must register with the Federal Tax Authority (FTA) and file annual returns, regardless of taxable income.
Challenges SMEs Face with Corporate Tax
| Challenge | Impact | Solution |
| Increased Administrative Costs | Filing returns and audits add expenses. | Leverage tax consultants and software. |
| Cash Flow Constraints | Tax payments may tighten cash reserves. | Plan tax payments in advance. |
| Lack of Awareness | Misunderstanding of compliance rules. | Educate SMEs through FTA workshops. |
Tax Benefits and Reliefs for SMEs
- 0% Tax Rate for Startups:
- SMEs below the income threshold benefit from the 0% rate, reducing their financial burden during early growth stages.
- Deductions for Business Expenses:
- Legitimate operating expenses, such as salaries, rent, and utilities, are deductible, lowering taxable income.
- Free Zone Advantages:
- Free Zone SMEs enjoy customs exemptions and may qualify for full tax relief on exports and specific activities.
- Relief for Loss-Making SMEs:
- Losses can be carried forward to offset future taxable income, easing the tax burden during recovery periods.
Sector-Specific Impacts on SMEs
| Sector | Impact of Corporate Tax |
| Retail and E-Commerce | May face tighter margins; deductions for inventory costs help. |
| Technology Startups | Benefit from 0% tax rate if income is below AED 375,000. |
| Real Estate SMEs | Rental income is taxable; however, Free Zone activities may qualify for exemptions. |
| Service Providers | Compliance costs increase, but expense deductions reduce taxable income. |
Steps for SMEs to Adapt to Corporate Tax
- Early Registration
- Register with the FTA to avoid late penalties and simplify compliance.
- Maintain Accurate Records
- Use accounting software to track income, expenses, and deductions.
- Seek Professional Advice
- Engage tax advisors to identify exemptions and minimize liabilities.
- Plan for Cash Flow
- Set aside funds for potential tax payments to avoid liquidity issues.
- Leverage Free Zone Benefits
- Relocate operations to Free Zones if the nature of business permits, to reduce tax liabilities.
Impact of Corporate Tax on SME Growth
| Aspect | Positive Effects | Negative Effects |
| Financial Discipline | Encourages better record-keeping and planning. | Adds to administrative burden. |
| Access to Funding | Transparent tax records attract investors. | Initial compliance costs may deter growth. |
| Market Competitiveness | Promotes a level playing field. | Smaller SMEs may face cost disadvantages. |
Corporate Tax Implications for UAE Real Estate Sector
The UAE real estate sector is a key driver of the economy, attracting both domestic and international investments. With the introduction of corporate tax, it’s important for businesses in the real estate sector to understand how the new tax framework will impact their operations.
Corporate Tax Overview for Real Estate Businesses in the UAE
- Tax Rate for Real Estate Businesses
- Real estate businesses in the UAE, whether involved in property development, rental, or management, will be subject to the new 9% corporate tax rate on annual profits exceeding AED 375,000.
- For businesses generating less than AED 375,000 in taxable income, there is no corporate tax.
- Taxable Income Sources
- Rental Income: Income derived from leasing properties will be taxed as part of the business’s overall taxable income.
- Capital Gains: Profits from selling real estate assets (e.g., land, buildings) will be taxed, though some exemptions may apply depending on the structure of the sale.
- Development Profits: Developers and construction companies will be taxed on profits derived from real estate development and sales.
Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) and Corporate Tax
- Tax Benefits for REITs
- Exemption: Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) that meet certain criteria may qualify for tax exemptions or a reduced tax rate, depending on the structure of their operations.
- Eligibility: To benefit from tax relief, REITs must comply with regulations on property management and profit distribution.
- Impact on Investors
- Investors in REITs will be subject to taxes on dividends received, though these can often be offset by tax deductions for related business expenses or reinvestment strategies.
Corporate Tax Exemptions in Free Zones for Real Estate
- Free Zone Real Estate
- Real estate businesses operating in specific Free Zones may benefit from a 0% tax rate for a specified period, often up to 50 years, as long as they meet certain conditions.
- Key Free Zones for Real Estate: Dubai International Financial Centre (DIFC), Abu Dhabi Global Market (ADGM), and others may offer tax incentives for real estate companies engaged in foreign investment or asset management.
- Free Zone Property Development
- Property developers in Free Zones can benefit from customs exemptions, as well as a range of other benefits, such as simplified licensing and access to international markets.
Deductions and Exemptions for Real Estate Businesses
- Deductible Expenses
- Real estate businesses can deduct various operating expenses, including:
- Property management costs
- Maintenance and repair expenses
- Employee salaries and benefits
- Marketing and advertising expenses
- Real estate businesses can deduct various operating expenses, including:
- Loss Carryforward
- Losses incurred by real estate businesses in one fiscal year can be carried forward to offset taxable income in subsequent years, reducing tax liabilities in profitable periods.
- Exemptions for Capital Gains
- Certain types of capital gains, especially those related to investments held for long periods, may be eligible for exemptions or reductions, depending on the transaction type and structure.
Challenges Faced by Real Estate Companies
| Challenge | Solution |
| Increased Administrative Burden | Real estate businesses should invest in accounting software or consult tax professionals to manage tax filing and reporting. |
| Non-compliance Risks | Ensure compliance with FTA regulations by regularly reviewing tax laws and seeking expert guidance. |
| Changes in Property Taxation Rules | Stay updated with the latest tax policies and understand which income sources are taxable. |
Steps Real Estate Companies Can Take to Navigate Corporate Tax
- Evaluate Taxable Income
- Understand which income streams are taxable and ensure accurate reporting. This includes rental income, capital gains, and development profits.
- Take Advantage of Deductions
- Maximize tax deductions by keeping detailed records of all business expenses related to property management and development.
- Explore Free Zone Benefits
- If feasible, consider relocating or expanding real estate operations in Free Zones to benefit from tax exemptions or reduced tax rates.
- Consult with Real Estate Tax Experts
- Work with tax professionals who specialize in real estate to optimize tax planning and ensure full compliance.
- Plan for Future Tax Changes
- The UAE’s tax policies are evolving. Regularly review and update your tax strategy to align with any legislative changes.
What UAE Tech Companies Need to Know About Corporate Tax
The UAE has emerged as a global hub for technology and innovation, attracting startups and established tech companies alike. With the introduction of corporate tax, it’s crucial for tech businesses to understand how the new tax rules affect their operations.
Tax Benefits and Exemptions for Tech Companies
- Free Zone Benefits
- Many UAE Free Zones, such as the Dubai Silicon Oasis and Abu Dhabi Global Market (ADGM), provide tax incentives for tech companies, including 0% corporate tax for up to 50 years, as long as certain conditions are met.
- Eligibility: To qualify, tech businesses must comply with the Free Zone’s regulations, which often require a focus on innovation and technology-driven activities.
- Research and Development (R&D) Deductions
- Tech companies engaged in R&D activities can benefit from tax deductions for expenses incurred in product development and technological innovation.
- Eligibility: To qualify for R&D deductions, businesses must document their R&D efforts and ensure the activities are aligned with FTA guidelines on innovation and development.
- Tax Relief for Startups
- Startups in the tech industry can benefit from the 0% corporate tax rate if their annual income is below AED 375,000, providing them with significant relief in the early years of growth.
- Capital Gains Tax Exemption
- In some cases, tech companies may be eligible for capital gains tax exemptions if they are involved in long-term investments in technology assets or intellectual property.
Implications of Corporate Tax on Tech Companies
- Increased Operational Costs
- Tech companies, particularly startups, may find it challenging to manage tax compliance costs, especially if they have not previously dealt with corporate tax filings.
- Solution: Leverage automated accounting and tax software to simplify compliance and reduce costs associated with tax filing.
- Cash Flow Management
- With the introduction of corporate tax, companies must plan for quarterly or annual tax payments, which could affect cash flow.
- Solution: Tech companies should set aside funds for tax liabilities, especially if they anticipate income exceeding the AED 375,000 threshold.
- Investor Considerations
- Investors may scrutinize tax liabilities as part of due diligence when funding tech companies. Understanding the tax structure and potential savings is critical to securing investment.
- Solution: Maintain transparent financial records and tax filings to present a clear financial picture to potential investors.
Key Deductions for Tech Companies
| Deduction | Impact |
| Research and Development (R&D) | Reduces taxable income by claiming R&D expenses, which can be substantial for tech companies. |
| Software and Equipment Costs | Allows tech companies to deduct the cost of software development, hardware, and other tech assets. |
| Employee Salaries and Benefits | Tech companies can deduct salaries and benefits provided to employees, which often make up a large portion of their operating costs. |
| Marketing and Advertising | Deducting advertising costs helps reduce taxable income, an essential benefit for tech companies expanding their market presence. |
How Tech Companies Can Maximize Tax Benefits
- Leverage Free Zone Advantages
- Consider setting up in a tech-focused Free Zone, such as Dubai Silicon Oasis or ADGM, to benefit from tax exemptions and other business incentives.
- Plan for R&D Deductions
- Maintain detailed records of R&D activities and expenses to maximize deductions and reduce taxable income.
- Take Advantage of Loss Carryforward
- If your tech business experiences losses in the early years, you can carry forward those losses to offset future taxable income, reducing future tax burdens.
- Seek Expert Tax Advice
- Given the complexities of tax regulations for tech companies, it is advisable to work with a tax consultant or accounting firm specializing in the tech sector. They can help you navigate tax planning, ensure compliance, and identify additional tax-saving opportunities.
How UAE Corporate Tax Affects the Economy
As one of the last major global economies without corporate tax, this policy change has wide-reaching implications for various sectors, businesses, and the overall economy.
Impact of Corporate Tax on the UAE Economy
- Diversification of Government Revenue
- The UAE’s reliance on oil revenues has been a central feature of its economy for decades. With the introduction of corporate tax, the government aims to diversify its revenue streams. Corporate tax is expected to generate significant income, reducing dependence on oil and contributing to a more balanced economy.
- Expected Revenue: The UAE government expects corporate tax to contribute billions of dirhams annually to the national budget, supporting social welfare programs, infrastructure development, and other public services.
- Boost to Public Infrastructure and Services
- Corporate tax revenue will enable the government to reinvest in essential public services such as healthcare, education, transportation, and technology infrastructure. The additional funding from corporate tax can improve the overall quality of life for residents and help attract foreign investment.
- Sectoral Impact: Investments in infrastructure will enhance the UAE’s position as a global business hub, encouraging further growth in sectors like tourism, logistics, and technology.
- Improved Fiscal Stability
- The introduction of corporate tax enhances fiscal stability by providing a consistent and sustainable source of government income. This move will reduce reliance on volatile oil prices and contribute to a more resilient economy.
- Long-term Planning: With a more diversified revenue base, the UAE government can better plan for future economic challenges, ensuring that essential services and economic development programs continue to thrive.
Impact on Business Dynamics
- Encouraging Business Compliance
- Corporate tax introduces a more structured tax environment that encourages businesses to comply with regulations and maintain transparent financial practices. This transparency is vital for attracting international investors who require stability and predictability in their investments.
- Enhanced Corporate Governance: With corporate tax, businesses are expected to adhere to stricter reporting standards, which can foster better corporate governance and accountability within the UAE’s business environment.
- Incentives for Business Innovation and Investment
- While corporate tax applies to businesses with profits above AED 375,000, the UAE government offers various tax incentives for innovation-driven businesses, including tax-free periods in Free Zones and R&D tax credits. This encourages businesses, particularly in sectors like tech, manufacturing, and healthcare, to invest in innovation and expand their operations.
- Long-term Investment: The tax benefits available for tech startups, SMEs, and larger enterprises create a favorable investment climate, encouraging both local and foreign businesses to invest in the UAE’s growing economy.
- Impact on SMEs and Startups
- For small and medium enterprises (SMEs) and startups, the 0% tax rate for businesses with taxable income under AED 375,000 provides significant financial relief. This allows smaller businesses to reinvest their earnings into growth initiatives such as expanding product offerings, increasing market reach, and hiring talent.
- Support for Emerging Sectors: Startups in sectors such as fintech, AI, and e-commerce stand to benefit greatly from the tax exemptions and incentives, spurring growth in these emerging industries.
Corporate Tax and Foreign Investment
- Attracting Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)
- The introduction of corporate tax can positively impact foreign direct investment (FDI) by signaling the UAE’s commitment to adhering to global standards of taxation and business transparency. While FDI has historically been attracted by the UAE’s tax-free environment, the new corporate tax regime is expected to provide greater stability and predictability for international investors.
- Tax Treaties: The UAE’s network of double taxation treaties, which have been expanded in recent years, will further strengthen its position as a preferred destination for foreign investment.
- Impact on Global Competitiveness
- The UAE continues to remain an attractive destination for foreign businesses due to its low corporate tax rate compared to other countries. The 9% tax rate is relatively low on the global scale, especially in comparison to corporate tax rates in other regions like Europe and North America. This makes the UAE a competitive jurisdiction for international businesses looking to expand in the Middle East.
- Free Zones: The availability of Free Zones with tax incentives and 0% tax rates for specific sectors will continue to make the UAE appealing for international companies seeking favorable tax conditions.
Challenges and Adjustments for the UAE Economy
| Challenge | Impact |
| Increased Cost of Doing Business | Corporate tax may increase operational costs for certain businesses, especially SMEs that have previously enjoyed a tax-free environment. |
| Potential Exodus of Low-Profit Firms | Some businesses, particularly low-margin companies, may find it challenging to adjust to the new tax regime, potentially relocating to more tax-friendly jurisdictions. |
| Shift in Economic Focus | The introduction of corporate tax could prompt a shift in economic focus from purely tax-exempt industries to those that offer broader value, such as technology and innovation. |
Corporate Tax and Large Businesses
- Impact on Multinational Corporations
- Compliance Complexity: Large corporations with global operations may face a more complex tax environment as they must comply with both UAE and international tax laws. These businesses will need to ensure that their tax strategy aligns with both local and global tax policies to avoid any conflicts or double taxation.
- Cross-Border Transactions: Multinational companies involved in cross-border transactions may need to reassess their structures to optimize for tax liabilities, leveraging international treaties, and transfer pricing strategies.
- Increased Transparency and Accountability
- With the introduction of corporate tax, businesses will be required to maintain higher levels of transparency and accountability in their financial operations. This could result in more accurate financial reporting, which enhances trust with investors, partners, and regulatory bodies.
- Investor Confidence: While the new tax regime might initially seem burdensome, it can ultimately lead to increased investor confidence, as businesses that comply with tax regulations are viewed as more stable and reliable.
VAT vs Corporate Tax: Key Differences in UAE
In the UAE, businesses are subject to different forms of taxation, primarily Value Added Tax (VAT) and Corporate Tax. While both taxes contribute to government revenue, they function in distinct ways and have different implications for businesses. Understanding the differences between VAT and corporate tax is essential for companies operating in the UAE, as it helps in tax planning, compliance, and financial forecasting.
What is VAT in the UAE?
Value Added Tax (VAT) is a consumption tax levied on the sale of goods and services. Introduced in the UAE in January 2018, VAT is charged at a standard rate of 5% on most goods and services, with certain exemptions and zero-rated items, such as healthcare and education. VAT is ultimately paid by the end consumer, but businesses are responsible for collecting and remitting it to the government.
- Taxable Events: VAT applies when a taxable supply of goods or services is made, when an import occurs, or when an invoice is issued.
- Input and Output VAT: Businesses charge VAT on their sales (output VAT) and can reclaim VAT on purchases (input VAT), provided they are VAT-registered.
Also checkout: VAT Calculator For UAE
Key Differences Between VAT and Corporate Tax
| Aspect | VAT | Corporate Tax |
| Type of Tax | Indirect Tax | Direct Tax |
| Who Pays the Tax? | End consumers pay VAT through businesses. | Businesses pay corporate tax on their profits. |
| Taxable Basis | Charged on the sale of goods and services. | Imposed on the profits of businesses. |
| Rate | Standard rate of 5%. | 9% on profits exceeding AED 375,000. |
| Collection and Payment | Businesses collect VAT from customers and remit it to the government. | Businesses pay corporate tax on their profits annually. |
| Exemptions | Exemptions on specific goods and services (e.g., healthcare, education). | Exemptions for certain Free Zone businesses and low-profit companies. |
| Threshold for Application | Applicable to businesses with taxable supplies exceeding AED 375,000 annually. | Applicable to businesses with profits exceeding AED 375,000. |
| Regulatory Requirements | VAT registration and reporting are required for businesses with annual supplies exceeding AED 375,000. | Corporate tax registration and compliance are required for businesses above the profit threshold. |
| Impact on Business Operations | VAT affects pricing, invoicing, and cash flow, as businesses must manage input and output VAT. | Corporate tax affects profitability and requires tax planning for deductions, exemptions, and structuring. |
Impact of VAT on Businesses
- Cash Flow and Pricing
- Since VAT is a consumption tax, businesses must charge VAT on sales and remit it to the government, which can impact cash flow, especially for companies with long payment cycles. Businesses need to manage VAT payments carefully to avoid liquidity issues.
- Price Adjustment: Businesses may adjust their prices to account for VAT, potentially making their goods and services more expensive for consumers.
- Administrative Burden
- VAT introduces an administrative burden for businesses, which must maintain accurate records of VAT paid and collected, file periodic VAT returns, and ensure compliance with tax regulations.
- Reclaiming VAT: Businesses can reclaim VAT on business-related purchases, which helps offset the VAT they collect on sales, but this requires detailed record-keeping and timely submission of VAT returns.
Also Read: VAT Returns and Refunds in UAE
How VAT and Corporate Tax Interact
While VAT and corporate tax are separate tax regimes, businesses may face both taxes simultaneously. This can lead to complex tax planning, as companies must ensure they are compliant with both VAT and corporate tax laws. Here are some key considerations for businesses:
- Dual Reporting
- Businesses will need to file separate returns for VAT and corporate tax. VAT is reported on a quarterly or monthly basis, while corporate tax is filed annually. Ensuring that both returns are accurate and timely is essential to avoid penalties.
- Tax Impact on Pricing and Profitability
- VAT affects the pricing of goods and services, while corporate tax affects the profitability of businesses. Both taxes need to be considered in pricing strategies, financial planning, and budgeting. Companies may need to adjust their cost structures or profit margins to account for both taxes.
- Compliance Risks
- Non-compliance with either VAT or corporate tax regulations can result in significant penalties and fines. It is essential for businesses to stay informed about the latest updates in tax policies and ensure they meet all regulatory requirements for both taxes.
Comparing Corporate Tax and Income Tax in UAE
The UAE has introduced a corporate tax regime, which represents a shift in its business tax landscape. However, one key distinction remains between corporate tax and income tax. In the past, the UAE did not impose income tax on individuals. Instead, the country relied on revenue from sectors like oil, gas, and real estate. With the introduction of corporate tax, understanding how it differs from income tax and what this means for businesses and individuals in the UAE is important for both local and foreign investors.
What is Income Tax in the UAE?
Income tax is a tax levied on an individual’s earnings, including salary, wages, and other forms of income. Historically, the UAE has been income tax-free for individuals, which made it a popular destination for expatriates and foreign workers. As a result, residents of the UAE have not been required to pay personal income tax on their earnings, unlike in many other countries where individuals are taxed based on their income levels.
- Taxable Event: Personal income, including salaries, wages, and other individual earnings, would be subject to income tax if it existed.
- Tax Rate: The UAE does not impose income tax on individuals at present, although some sectors (e.g., oil and gas companies or foreign bank branches) may have specific taxes or royalties on their operations.
Key Differences Between Corporate Tax and Income Tax
| Aspect | Corporate Tax | Income Tax |
| Who Pays the Tax? | Businesses, including companies, branches, and other entities. | Individuals earning income, such as salaries and wages. |
| Taxable Basis | Taxed on profits generated by the business. | Taxed on the income earned by individuals (e.g., salary, wages). |
| Tax Rate | 9% on profits exceeding AED 375,000. | There is no personal income tax in the UAE. |
| Exemptions | Free zone businesses may have exemptions. | Exempt from personal income tax in the UAE. |
| Scope of Application | Corporate tax applies to business profits. | Income tax applies to personal earnings (if implemented). |
| Collection Method | Companies collect and pay corporate tax to the government. | Individuals would pay income tax through payroll deductions (if applied). |
| Regulatory Compliance | Businesses must file annual tax returns and maintain records of profits and expenses. | No personal tax filings required as there is no income tax. |
| Global Comparison | Similar to corporate taxes in other countries (e.g., USA, UK). | Common in most countries, with varying rates depending on income levels. |
What Does Income Tax (If Introduced) Mean for Individuals?
- Potential Impact on Salaries
If the UAE were to introduce income tax, individuals would be required to pay tax on their earnings. This would likely lead to a reduction in disposable income, as employees would need to account for deductions from their salaries.- Tax Brackets: If introduced, income tax in the UAE would likely have different rates based on income levels, with higher earners paying a larger percentage of their income in tax.
- Attraction for Foreign Talent
The absence of income tax in the UAE has been a key factor in attracting expatriates and foreign workers. The introduction of income tax could alter the attractiveness of the UAE as a destination for global talent, especially if the tax rates are high compared to other countries. - Personal Financial Planning
Individuals would need to plan for their personal taxes, including saving for tax payments and adjusting their spending habits based on their after-tax income. This could lead to a greater demand for financial advisory services to help individuals navigate personal tax obligations.
UAE Corporate Tax Audits: What to Expect
As part of the UAE’s corporate tax regime, businesses are required to maintain compliance with tax laws. To ensure transparency and correct reporting, the Federal Tax Authority (FTA) conducts corporate tax audits. These audits are essential to verifying that businesses are accurately reporting their taxable profits and adhering to tax obligations.
What is a Corporate Tax Audit in the UAE?
A corporate tax audit is a review or examination conducted by the FTA to assess whether a company’s financial records, tax filings, and payment of taxes are accurate and in compliance with UAE tax regulations. The goal of the audit is to ensure that businesses are reporting their taxable income and expenses correctly and paying the appropriate amount of corporate tax.
FTA tax audits can be triggered for various reasons, such as discrepancies in tax filings, random selection, or suspicion of non-compliance. The UAE tax authority has the right to audit businesses to confirm their tax positions and enforce tax regulations.
Reasons for a Corporate Tax Audit
- Random Selection
The FTA may randomly select businesses for tax audits as part of their compliance monitoring efforts. Random audits are designed to ensure that companies are abiding by tax laws even without any obvious signs of wrongdoing. - Suspicion of Non-Compliance
If a business has discrepancies in its tax filings, such as significantly underreported profits or exaggerated deductions, the FTA may initiate an audit. This is to verify that the business is complying with the corporate tax requirements. - Tax Return Red Flags
Businesses with a history of errors, frequent adjustments to tax returns, or a significant number of amendments to previously filed returns might trigger an audit. The FTA often reviews returns for inconsistencies or anomalies. - Transfer Pricing Concerns
Companies that engage in cross-border transactions or have related-party dealings may be subject to more scrutiny. If the FTA suspects that transfer pricing is not in line with the arm’s length principle, they may conduct a more detailed audit.
What to Expect During a Corporate Tax Audit in the UAE
- Initial Notification
Once the FTA selects a business for a tax audit, they will send an official notification. This notice will specify the start date of the audit, the time period being reviewed, and any documents or records that need to be provided.- Notice Period: Typically, businesses will receive a 15-day notice before the audit begins. The notification will list the required documentation, including financial statements, tax returns, and supporting records.
- Document Review
During the audit, the FTA will review various financial documents to ensure that the tax filings are accurate. These documents may include:- Income statements
- Balance sheets
- Bank statements
- Invoices and receipts
- Contracts (especially intercompany contracts for transfer pricing)
- Tax returns (including annual returns and amended returns, if applicable)
- The FTA will verify that the company has reported the correct amount of income, claimed valid deductions, and paid the proper amount of corporate tax.
- Interviews and Explanations
The auditors may request interviews with senior management, accountants, or other key personnel. This step is to clarify certain transactions, ask for explanations of complex financial matters, or address discrepancies in the records.- Be prepared to explain any unusual or significant transactions, especially those involving intercompany dealings or cross-border payments.
- On-Site Inspection
Depending on the nature of the audit, FTA auditors may visit the business premises to inspect the company’s records. This could involve reviewing physical documents or accessing digital records stored on internal systems. - Tax Adjustments and Penalties
After reviewing the records, the FTA may make tax adjustments if discrepancies are found. If the company has underpaid taxes or claimed invalid deductions, the FTA will issue a revised tax assessment.- Penalties may also apply, including fines for underpayment, late payment of taxes, or failure to maintain proper records.
- The FTA may impose interest charges on any unpaid taxes, which can accumulate over time.
- Audit Conclusion
Once the audit is complete, the FTA will issue an audit report detailing their findings. The business will have the opportunity to review the findings and, if necessary, contest the assessment before paying any additional taxes or penalties.- Taxpayer’s Right to Appeal: If the business disagrees with the findings, it can appeal the decision within 40 days from receiving the audit report.
How to Prepare for a Corporate Tax Audit in the UAE
- Keep Accurate and Organized Records
Proper record-keeping is crucial for any business. Maintain all financial records, including invoices, receipts, contracts, and bank statements, for a minimum of 5 years as required by UAE tax law. Ensure that the records are organized and easily accessible in case of an audit. - Ensure Compliance with Transfer Pricing Rules
If your company operates internationally or has related-party transactions, ensure compliance with transfer pricing documentation. Make sure all intercompany transactions follow the arm’s length principle, and keep detailed documentation to support these transactions. - Conduct Regular Internal Audits
Regular internal audits will help identify any discrepancies before the FTA audits your company. Internal audits also allow you to review your tax filing practices and ensure compliance with the corporate tax laws. - Review Tax Returns Before Filing
Double-check your tax returns before filing them with the FTA. Make sure they are accurate, complete, and reflect the correct financial information. Any errors or omissions can trigger an audit or lead to penalties. - Consult with Tax Professionals
To avoid errors and improve your chances of passing the audit with minimal issues, consult with a tax advisor or accountant. Professionals can help ensure that your tax returns are correctly prepared, your financial records are in order, and that you comply with the UAE’s tax regulations.
What Happens After the Audit?
Once the audit is concluded, the FTA will issue an assessment based on their findings. Depending on the results, you may have to make additional tax payments, pay penalties, or appeal the decision if you believe it is incorrect. If everything is in order, the business will receive a clean audit report and will continue its operations as usual.
- Tax Assessment: The FTA will issue an assessment, which outlines the tax due based on their review. This could include the corporate tax owed, penalties, and interest for late payments.
- Payment of Taxes: Once the audit report is issued, the business must pay the additional taxes and penalties within the specified deadline. Failure to do so can lead to further fines and enforcement actions.
- Appeals Process: If the business disagrees with the audit findings, it has the right to file an appeal. The appeal must be submitted to the FTA within 40 days from receiving the audit results.
Ensuring Corporate Tax Compliance in the UAE
It is crucial for businesses to understand their responsibilities and take steps to ensure compliance. Failing to meet corporate tax obligations can lead to penalties, interest charges, and other consequences that could harm a business’s financial standing and reputation.
Key Steps for Ensuring Corporate Tax Compliance
- Register with the UAE Federal Tax Authority (FTA)
Businesses must register with the UAE Federal Tax Authority (FTA) once they meet the requirements for corporate tax. Failure to register can result in fines, so it is essential to submit the registration application as soon as your business becomes liable for tax. Businesses are required to:- Submit the tax registration application with the FTA.
- Provide all relevant documentation, such as the business’s legal entity status, financial details, and ownership structure.
- Obtain a tax registration number (TRN) once the registration process is complete.
- File Corporate Tax Returns on Time
One of the most critical aspects of corporate tax compliance is the timely submission of tax returns. The UAE requires businesses to file their tax returns annually, typically within nine months from the end of the financial year. Failing to file returns on time can result in substantial late fees and penalties.
Best Practices:- Set up a tax calendar to track key filing deadlines.
- File returns electronically through the FTA’s e-Services portal.
- Double-check the financial records to ensure the information is accurate before submitting.
- Ensure Accurate Reporting of Taxable Income and Expenses
For corporate tax compliance, it is essential that businesses accurately report their taxable income, allowable expenses, and other tax-related items. The tax authority will assess the financial records to ensure that the reported income is in line with the company’s actual earnings. Common areas where mistakes may arise include:- Revenue reporting: Ensure that all revenue streams are accounted for correctly.
- Expense deductions: Claim only legitimate business expenses in accordance with the tax code.
- Adjustments and credits: Verify that any adjustments or credits are properly applied and supported by documentation.
- Maintain Proper Documentation and Record-Keeping
Proper documentation is essential for tax compliance. The UAE requires businesses to maintain detailed financial records for a minimum of five years from the date of the tax return. These records should include:- Invoices and receipts for sales and purchases.
- Contracts and agreements, especially for related-party transactions.
- Bank statements and other supporting documents.
- Payroll records to demonstrate compliance with payroll tax laws.
- Financial statements like income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements.
- Adhere to Transfer Pricing Rules
Businesses involved in cross-border transactions or with related parties must comply with the UAE’s transfer pricing rules. The FTA requires businesses to follow the arm’s length principle for intercompany transactions, meaning that transactions between related parties should be priced as if they were conducted between unrelated parties.
Requirements:- Transfer pricing documentation: Businesses must maintain and submit documentation to support the pricing of intercompany transactions.
- Local file: Companies must prepare and maintain a local file documenting intercompany transactions in accordance with FTA requirements.
- Master file: A global master file may be required for large businesses with complex international operations.
- Ensure Timely Payment of Corporate Tax
After filing tax returns, businesses are required to pay any taxes due within the specified time frame. Delayed payments can result in interest charges and penalties, which can add up quickly. Here are some steps businesses can take to ensure timely payments:- Understand the tax liability: Accurately calculate your tax liability based on the assessed taxable income.
- Monitor due dates: Track payment deadlines and avoid missing the due date.
- Use online payment options: The FTA allows businesses to make payments via their e-Services portal, which streamlines the process.
- Stay Updated on Corporate Tax Law Changes
Tax laws and regulations in the UAE may change over time. It’s important for businesses to stay updated on any amendments to corporate tax policies, especially those that may impact their filing procedures or tax obligations.
Best Practices:- Subscribe to FTA updates or newsletters for the latest information on tax changes.
- Attend tax seminars or webinars to stay informed about regulatory updates.
- Consult with tax advisors to ensure that your business is in compliance with the latest changes.
- Use Professional Tax Services
Corporate tax compliance can be complex, especially for businesses with international operations or intricate financial structures. Hiring a qualified tax professional or advisor can help ensure compliance and reduce the risk of mistakes that could lead to penalties or audits.
Services provided by tax professionals:- Tax filing assistance: Preparing and submitting corporate tax returns on time.
- Tax strategy and planning: Helping businesses reduce their tax liabilities through legal tax-saving strategies.
- Audit support: Assisting with audits and helping businesses navigate any challenges from the tax authorities.
- Transfer pricing consultation: Ensuring compliance with intercompany transaction rules.
Expert Tips for Corporate Tax Planning in the UAE
Corporate tax planning is a critical aspect of running a business in the UAE. With the introduction of a corporate tax regime, businesses must adopt effective tax strategies to minimize their tax liabilities, ensure compliance with regulations, and optimize their financial performance. Proper tax planning can help businesses take advantage of exemptions, deductions, and incentives offered by the UAE’s tax system, as well as avoid common pitfalls that could lead to penalties or audits.
1. Understand the UAE Corporate Tax System Thoroughly
The first step in effective corporate tax planning is to fully understand the corporate tax system in the UAE. The introduction of corporate tax means businesses will be subject to a 9% tax on profits exceeding AED 375,000. However, various exemptions and incentives may apply based on the nature of the business, the industry, or the location.
Key points to consider:
- Tax Rate: The 9% corporate tax rate applies to profits over AED 375,000. Profits below this threshold are not taxed.
- Free Zones: Businesses operating in UAE Free Zones may be eligible for tax exemptions for a certain period, depending on the free zone’s regulations and the type of business activity.
- Industry-Specific Tax Reliefs: Some sectors, such as tech and renewable energy, may be eligible for tax incentives or exemptions.
Tip: Stay informed about the corporate tax rate, exemptions, and special provisions that may apply to your business. Consulting a tax advisor is crucial to understanding how the laws affect your specific industry.
2. Plan for Transfer Pricing Compliance
For businesses with international operations or those engaged in intercompany transactions, transfer pricing compliance is a key aspect of tax planning. The UAE requires that transfer prices between related parties be set in accordance with the arm’s length principle, meaning that transactions should be priced as if they were between unrelated parties.
Effective planning strategies:
- Document Transfer Pricing Policies: Maintain comprehensive records to support transfer pricing policies and ensure that they align with the arm’s length principle.
- Prepare Transfer Pricing Reports: Companies involved in cross-border transactions should prepare a local file and master file to comply with the documentation requirements of the UAE tax system.
- Review Pricing Structures Regularly: Conduct periodic reviews of intercompany pricing to ensure they reflect market conditions and comply with tax regulations.
Tip: Work with a transfer pricing expert to structure intercompany transactions in a way that minimizes tax liabilities while remaining compliant with the UAE’s rules.
3. Take Advantage of Tax Incentives and Exemptions
The UAE offers several tax incentives and exemptions for businesses operating in certain sectors or regions. These incentives can significantly reduce your overall tax liability. Some examples of tax incentives include:
- Free Zone Benefits: Companies established in UAE Free Zones may be eligible for tax holidays of up to 50 years, depending on the nature of their business activities and the specific free zone.
- R&D Tax Relief: Some industries, such as technology and manufacturing, may be eligible for research and development (R&D) tax credits or deductions, reducing taxable income.
- Capital Allowances: Businesses may qualify for capital allowances for certain capital expenditures, such as investments in machinery, technology, or office buildings.
Tip: Explore the tax incentives available for your industry and business model. You may qualify for deductions, exemptions, or credits that can significantly reduce your corporate tax liability.
4. Ensure Proper Record-Keeping for Accurate Reporting
Effective tax planning requires keeping detailed and accurate financial records. The UAE’s corporate tax system requires businesses to maintain their books and records for at least five years from the end of the tax period. Failure to maintain proper documentation can lead to errors in tax filing, penalties, or audits.
Best practices for record-keeping:
- Use Accounting Software: Adopt reliable accounting software to streamline the process of tracking income, expenses, and tax-related transactions.
- Maintain Detailed Invoices and Contracts: Keep a comprehensive record of all invoices, contracts, and agreements, particularly those related to intercompany transactions, capital expenditures, and deductible expenses.
- Retain Supporting Documents: Ensure that supporting documents for tax returns—such as bank statements, receipts, and purchase orders—are easily accessible for filing and audit purposes.
Tip: Regularly update your financial records to reflect accurate and up-to-date information. This will help ensure that your tax returns are correct and compliant.
5. Timing of Tax Payments and Filing
Managing the timing of tax payments and tax filings is another critical aspect of corporate tax planning. Businesses must submit their corporate tax returns within nine months of the end of their fiscal year. Failure to file on time can lead to late payment penalties and interest charges.
Tips for managing tax timing:
- Set Up a Payment Schedule: Plan your tax payments ahead of time by setting up a payment schedule aligned with tax deadlines. This will help ensure that you don’t miss key dates.
- File Early: Aim to file your corporate tax returns early to avoid last-minute errors or complications.
- Utilize the FTA’s E-Services Portal: The FTA provides an online platform for filing and paying taxes. Make use of this portal to file your returns and pay taxes conveniently and on time.
Tip: Setting up automated reminders or using accounting software to track tax deadlines can help you avoid late filings and payments.
6. Explore Tax Optimization Strategies
Corporate tax planning isn’t just about minimizing tax liabilities; it’s also about optimizing the overall tax structure to ensure that taxes are managed efficiently. Tax optimization strategies can help reduce taxes in a sustainable manner without violating the law.
Popular tax optimization techniques:
- Holding Company Structure: Consider setting up a holding company in a UAE Free Zone to benefit from tax exemptions and minimize the tax burden on foreign subsidiaries.
- Loss Carryforwards: Use tax-loss carryforwards to offset taxable income in future years. This can be beneficial if your business has incurred losses in prior years that can be deducted against future profits.
- Group Relief: If you have multiple entities, consider taking advantage of group relief provisions, where losses from one company can be offset against profits from another.
Tip: Work with a tax planner to explore the best tax optimization strategies for your business. A tailored approach can help reduce the overall tax burden while ensuring compliance with UAE regulations.
7. Regularly Review and Update Your Tax Plan
Corporate tax planning is not a one-time activity but an ongoing process. Regular reviews of your tax strategy are essential to ensure that it continues to meet the needs of your business and aligns with any changes in tax laws.
Review strategies:
- Annual Tax Reviews: Conduct an annual tax review to assess your current tax position and determine whether any adjustments are needed.
- Monitor Regulatory Changes: Keep up with any changes in UAE tax regulations, including amendments to corporate tax rates, new tax credits, or additional exemptions.
- Adapt to Business Changes: As your business grows or enters new markets, your tax planning strategy should be adjusted to reflect new business models or expansion.
Tip: Stay proactive in reviewing your tax planning strategy to ensure it evolves in line with both your business needs and changes in tax laws.
How to Save on Corporate Taxes in the UAE
Corporate tax savings are essential for businesses aiming to optimize their financial performance and maintain competitive advantage. The introduction of corporate tax in the UAE has changed the landscape for businesses, but it also opens up a range of opportunities for tax savings if companies strategically plan their finances and operations.
1. Leverage Free Zone Tax Benefits
One of the most effective ways to reduce corporate tax liabilities in the UAE is by taking advantage of the many Free Zones available across the country. These zones offer businesses various tax incentives, including tax holidays and exemptions, which can significantly reduce the tax burden.
Free Zone Benefits:
- Tax Exemptions: Many Free Zones offer tax-free periods ranging from 15 to 50 years, depending on the location and type of business.
- 100% Ownership: Companies in Free Zones are allowed 100% foreign ownership, which eliminates the need for a local partner.
- No Import/Export Duties: Certain Free Zones provide duty exemptions on imports and exports, which further reduce the financial burden on businesses.
2. Maximize Depreciation Deductions
The UAE corporate tax system allows businesses to claim depreciation on capital assets such as machinery, office equipment, and property used for business operations. By maximizing these deductions, businesses can reduce their taxable income, thus lowering their tax liability.
Depreciation Deductions Strategy:
- Full Utilization of Depreciation: Ensure that all eligible business assets are depreciated to the maximum allowed extent over their useful life.
- Accelerate Depreciation: Certain assets can be depreciated more quickly depending on their classification under the UAE tax rules. Investigate the possibility of accelerating depreciation on assets like computers or vehicles, which can help reduce taxable profits in the short term.
Tip: Consult with your accountant to ensure that your depreciation strategy is optimized and aligned with current tax regulations.
3. Capital Losses and Carryforwards
In the event that your business incurs capital losses, you can use these losses to offset future profits, which will lower the amount of tax you owe in profitable years. The UAE allows businesses to carry forward losses to offset taxable income in subsequent years.
Capital Loss Carryforward Strategy:
- Track Losses: Keep detailed records of any capital losses your business incurs to ensure they can be carried forward into future tax periods.
- Offset Future Profits: In years when your business is profitable, use the carried-forward losses to reduce taxable income and minimize your tax liability.
Tip: If your business faces cyclical or seasonal income fluctuations, carryforward provisions allow you to smooth out tax liabilities over time.
4. Explore Tax Incentives for Research and Development (R&D)
For companies involved in research and development (R&D), the UAE offers tax credits or deductions for qualifying expenses. Businesses in sectors like technology, pharmaceuticals, and manufacturing that engage in innovative activities may be eligible for tax breaks on R&D spending.
R&D Tax Incentive Strategy:
- Claim Deductions: Track and document all R&D expenditures, including salaries, materials, and equipment used for research activities. Ensure that these are claimed as deductions to reduce taxable income.
- Stay Informed About Incentives: R&D incentives and credits may evolve, so it’s important to regularly check for any new opportunities or government programs available for innovation.
Tip: Establish a dedicated R&D team or department to ensure that your business can maximize the available incentives and claim all eligible expenses.
5. Implement Transfer Pricing Best Practices
For businesses with international operations or transactions between related entities, transfer pricing optimization is a critical strategy for tax savings. The UAE requires businesses to adhere to the arm’s length principle, ensuring that intercompany transactions are priced fairly and comply with international tax standards.
Transfer Pricing Strategy:
- Document Transfer Pricing Policies: Maintain proper documentation of your transfer pricing policies and related party transactions. This ensures compliance with UAE regulations and can protect your business in case of an audit.
- Review Pricing Regularly: Regularly review your pricing models for intercompany transactions to ensure that they are still within market rates and align with tax regulations.
Tip: Engaging with a transfer pricing expert can help you develop a tax-efficient structure for intercompany transactions while remaining compliant.
6. Take Advantage of Holding Company Structures
If your business has multiple subsidiaries or investments, setting up a holding company structure in the UAE can offer significant tax savings. Holding companies can receive tax-free dividends and capital gains from subsidiaries, which reduces the overall tax liability.
Holding Company Optimization Strategy:
- Create a Holding Company: If you operate in multiple sectors or countries, consider setting up a holding company in a UAE Free Zone or mainland to centralize ownership and control of your subsidiaries.
- Tax-free Dividends: Holding companies can typically receive dividends from their subsidiaries without incurring additional tax, which can be reinvested or distributed to shareholders without a tax penalty.
Tip: Review your corporate structure to determine if a holding company could benefit your business, especially if you have multiple divisions or entities.
7. Employee Incentive Programs
Tax savings are not only about reducing the tax burden on profits but also include incentivizing employees. Offering employees tax-efficient compensation packages, such as stock options, bonuses, or profit-sharing, can help reduce taxable income while improving employee retention and motivation.
Employee Incentive Strategy:
- Use Stock Options: Offering stock options to employees can be a way to incentivize staff while minimizing the immediate tax burden on the company.
- Profit-Sharing Plans: Establish profit-sharing programs where employees receive a share of the company’s profits, which is a deductible expense for the business.
Tip: Structure employee compensation in a tax-efficient way to reduce tax liabilities while ensuring that your incentive programs remain attractive to top talent.
8. Monitor Tax Deadlines and Filing Procedures
Failing to comply with corporate tax filing deadlines can lead to penalties and interest charges, which could increase the overall tax burden. Ensuring that your tax filings are completed on time is an essential part of managing your tax obligations and saving on penalties.
Tax Filing Optimization Strategy:
- Stay on Top of Deadlines: Ensure you are aware of the tax filing deadlines and submit your returns on time to avoid late payment penalties.
- Use the FTA Portal: The Federal Tax Authority (FTA) provides an online portal for filing taxes and paying dues. Using this system ensures you meet deadlines and reduce the risk of errors.
Tip: Set reminders for filing deadlines or use accounting software to track and submit your corporate tax returns well in advance.
9. Consult with Tax Professionals
Finally, one of the most effective ways to save on corporate taxes is to work with tax professionals who are familiar with the intricacies of the UAE’s corporate tax system. Tax advisors can provide tailored advice to help you navigate the complexities of tax laws, identify eligible tax-saving opportunities, and ensure compliance.
Tax Professional Strategy:
- Engage with Experts: Work closely with tax consultants or accountants who are familiar with the UAE corporate tax landscape to ensure that you are taking full advantage of all available tax-saving opportunities.
- Ongoing Tax Advice: Regular consultations with tax professionals will help you stay updated on changes to tax laws and optimize your strategy accordingly.
Tip: Choose a tax advisor who understands your industry and business structure to get personalized advice on how to save on taxes.
What’s New in UAE Corporate Tax Policies
The introduction of a 9% corporate tax rate for businesses that meet specific thresholds, marking a major shift in the country’s fiscal landscape. This new policy, which came into effect in June 2023, was designed to align the UAE’s tax system with international standards and promote economic diversification.
Here we’ll explore the new corporate tax policies in the UAE, the implications for businesses, and key changes to watch for in the coming years.
1. Introduction of Corporate Tax Rate
Before June 2023, the UAE was one of the few countries in the world with no corporate tax on most businesses, a feature that attracted many international companies and investors. However, with the UAE’s transition to a corporate tax system, a 9% tax on profits exceeding AED 375,000 was implemented.
Key Points:
- 9% Tax Rate: The standard corporate tax rate is 9% on profits exceeding AED 375,000. For profits below this threshold, businesses are exempt from corporate tax.
- Progressive Tax System: The introduction of the 9% tax is a progressive move to ensure that the UAE remains competitive while fulfilling its international obligations and diversifying its revenue sources.
2. VAT Remains Unchanged
While the introduction of corporate tax has been a significant development, the Value-Added Tax (VAT) in the UAE remains unchanged. The VAT rate of 5% continues to apply to most goods and services, providing businesses with a clear tax structure for both consumption and corporate activities.
Key Points:
- 5% VAT Rate: The VAT system, introduced in 2018, remains in effect for businesses offering taxable goods and services.
- VAT Registration: Companies with a turnover of over AED 375,000 annually are required to register for VAT. Businesses below this threshold can voluntarily register for VAT.
3. Corporate Tax Exemptions for Free Zones
The UAE continues to offer significant tax benefits for businesses operating within its Free Zones. Companies established in Free Zones benefit from tax exemptions for a specific period, ranging from 15 to 50 years. These zones are a critical aspect of the UAE’s strategy to attract foreign investment and support economic diversification.
Key Points:
- No Corporate Tax: Businesses in most Free Zones are still exempt from corporate tax for a fixed period.
- Specific Business Activities: Companies engaged in certain activities, such as technology, manufacturing, logistics, and finance, may benefit from tax exemptions or reduced tax rates, even if they exceed the AED 375,000 threshold.
4. Transfer Pricing and International Tax Compliance
With the implementation of corporate tax, the UAE has also aligned itself with global standards regarding transfer pricing. Businesses engaging in cross-border transactions with related parties must adhere to arm’s length principles to ensure that pricing for transactions between related entities is in line with market standards.
Key Points:
- Transfer Pricing Rules: Businesses involved in international trade or transactions between subsidiaries must document transfer pricing arrangements and ensure compliance with UAE regulations.
- OECD Guidelines: The UAE’s transfer pricing rules follow the OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development) guidelines to maintain fair and transparent pricing structures for intercompany transactions.
5. Tax Loss Carryforward and Carryback Provisions
The UAE corporate tax policy allows businesses to carry forward tax losses to offset future taxable profits. This is particularly beneficial for startups or businesses experiencing losses during the early years of operation.
Key Points:
- Loss Carryforward: Businesses can carry forward losses from one year to offset taxable income in future years.
- No Carryback Provisions: The UAE’s tax policy does not allow businesses to carry losses back to offset taxes paid in previous years.
6. Digital Economy and Technology Sector Incentives
The UAE has continued its push to support the digital economy and technology sector through favorable corporate tax policies. The government recognizes the importance of sectors like technology, fintech, and innovation in driving future economic growth.
Key Points:
- Tax Breaks for Tech Companies: Tech companies can benefit from the UAE’s attractive Free Zone incentives and may qualify for additional tax exemptions in specific sectors, such as artificial intelligence and blockchain.
- R&D Deductions: The UAE government encourages companies involved in research and development (R&D) through tax deductions for R&D expenses, which can significantly reduce tax liabilities.
7. Impact of Corporate Tax on SMEs
While large corporations are typically the focus of corporate tax discussions, the UAE’s new corporate tax system also has implications for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). SMEs with profits below AED 375,000 are exempt from corporate tax, providing relief to a key segment of the UAE economy.
Key Points:
- Exemption for Small Profits: SMEs that generate less than AED 375,000 in annual profits are exempt from corporate tax.
- Gradual Transition: Some tax reforms may gradually phase in, ensuring that SMEs can adjust to the new system over time.
8. Enhanced Tax Filing and Reporting Requirements
As part of its compliance with global tax standards, the UAE has introduced enhanced tax filing and reporting requirements. Companies now need to submit detailed financial statements, tax returns, and, in some cases, transfer pricing documentation.
Key Points:
- Annual Filings: Corporate tax returns must be filed annually, with supporting documentation for income, expenses, and tax deductions.
- Digital Filing: The UAE’s Federal Tax Authority (FTA) provides an online portal for filing corporate tax returns, ensuring a streamlined and efficient process..
9. Continued Focus on Economic Diversification
The introduction of corporate tax aligns with the UAE’s broader goal of economic diversification. The government aims to reduce its reliance on oil revenues and has made strides to boost other sectors, such as tourism, technology, and finance, by offering attractive tax policies for businesses in these areas.
Key Points:
- Diversification Initiatives: Corporate tax revenues will support the UAE’s diversification efforts, funding initiatives that promote sectors beyond oil and gas.
- Sustainability Incentives: The UAE also offers incentives for businesses that invest in sustainable practices or green technologies, further aligning with global trends.


