How to file taxes for MLM business (2024)

Navigating the tax landscape for your MLM (Multi-Level Marketing) business is crucial for maintaining financial health and compliance. As the tax season approaches in 2024, understanding the specific considerations for your MLM venture becomes paramount. The unique structure of MLM businesses introduces complexities that necessitate a comprehensive approach to filing taxes.
In this guide, we will delve into key aspects, such as income reporting, deductions, and compliance requirements, providing you with valuable insights on how to effectively navigate the tax implications of your MLM business in the year 2024. By the end of this guide, you’ll be better equipped to ensure your tax obligations are met while optimizing your financial outcomes within the MLM framework.
Table of Contents
What is Multi-Level Marketing (MLM)
Multi-level marketing (MLM), or network marketing or pyramid selling, is a business strategy in which a company recruits independent distributors to sell its products or services. These distributors earn commissions on their sales and the sales made by the distributors they recruit into the network. This creates a multi-level structure, or a “downline,” with compensation flowing up the chain from the sales generated by individuals at various levels.
MLM companies typically operate on a tiered commission system, where distributors earn money not only from their direct sales but also from the sales made by those they have recruited (referred to as their “downline”) and by subsequent levels of recruits. The structure often resembles a pyramid, with the top representing the company and the levels below representing the distributors at different tiers.
While MLM has been successful for some individuals and companies, it has also been controversial and criticized. Some critics argue that the structure can resemble a pyramid scheme, which is illegal in many jurisdictions. It’s important for individuals considering involvement in an MLM business to carefully research the company and its compensation plan to understand how income is generated and whether the business model is sustainable and ethical.
Importance of tax filing for MLM businesses
Running a Multi-Level Marketing (MLM) business comes with unique financial considerations, and tax filing plays a pivotal role in ensuring the longevity and compliance of such ventures. Here are key reasons why meticulous tax filing is crucial for MLM businesses:
1. Compliance and Legal Obligations:
MLM businesses are subject to the same tax laws and regulations as any other business entity. Proper tax filing ensures compliance with local, state, and federal tax requirements, helping the business operate within the bounds of the law.
2. Avoiding Legal Issues:
Non-compliance with tax regulations can lead to legal troubles and penalties. Filing taxes accurately and on time helps prevent legal complications that could harm the reputation and financial stability of the MLM business.
3. Transparent Financial Reporting:
Accurate tax filing provides a clear picture of the MLM business’s financial health. This transparency is not only essential for regulatory compliance but also aids in making informed business decisions and attracting potential investors or partners.
4. Maximizing Deductions:
MLM entrepreneurs may be eligible for various tax deductions related to business expenses, marketing costs, and home office deductions. Filing taxes diligently allows businesses to maximize these deductions, reducing the overall tax liability and increasing profitability.
5. Building Credibility:
A well-documented and compliant tax history enhances the credibility of an MLM business. This can be important when dealing with financial institutions, partners, or potential recruits who may scrutinize the business’s financial practices.
6. Risk Mitigation:
Proper tax filing helps identify potential risks and areas of concern. By addressing these issues promptly, MLM businesses can mitigate financial risks and ensure long-term sustainability.
7. Financial Planning:
Tax filing is an integral part of the overall financial planning for an MLM business. It provides insights into cash flow, profits, and areas for improvement, enabling better strategic planning and resource allocation.
8. Avoiding Audits:
Accurate and timely tax filing reduces the likelihood of being audited by tax authorities. Being prepared and organized with financial records can streamline the auditing process if it does occur.
The importance of tax filing for MLM businesses extends beyond mere compliance; it is a strategic and essential aspect of maintaining financial health, legal standing, and credibility within the dynamic landscape of network marketing.
Understanding Taxable Income in MLM

In the context of Multi-Level Marketing (MLM), gross income encompasses the total earnings generated by an individual or business before deducting expenses. For MLM entrepreneurs, gross income comprises two primary components:
1. Retail Profits:
- Definition: This includes profits earned from the direct sale of products or services to end consumers.
- Tax Implications: Retail profits are part of the gross income and are subject to taxation. MLM participants should maintain accurate records of these sales to report the income correctly.
2. Commissions Earned:
- Definition: Commissions represent the earnings derived from the sales made by the distributor’s downline or team.
- Tax Implications: Commissions contribute to the gross income and are also subject to taxation. Proper documentation of downline sales and commission structures is crucial for accurate tax reporting.
Retail Profits vs. Commissions Earned in MLM:
1. Retail Profits:
- Nature: Direct sales to end consumers.
- Tax Treatment: Taxable as part of the overall gross income.
- Documentation: Maintain records of retail transactions, including sales receipts and customer information.
2. Commissions Earned:
- Nature: Indirect earnings from downline sales.
- Tax Treatment: Counted as income and subject to taxation.
- Documentation: Keep detailed records of downline sales, commission structures, and any bonuses received.
Importance of Tracking Deductions and Expenses:
1. Maximizing Deductions:
- MLM entrepreneurs can deduct legitimate business expenses to reduce their taxable income. This includes expenses such as marketing materials, travel costs for business-related events, and a portion of home office expenses.
2. Accurate Expense Tracking:
- Maintaining precise records of business-related expenses is crucial for proper tax reporting. This includes receipts, invoices, and documentation supporting each deductible expense.
3. Tax Efficiency:
- Tracking deductions enhances tax efficiency by reducing the overall tax liability. It allows MLM business owners to retain more of their earnings for reinvestment or personal use.
4. Audit Preparedness:
- Thorough documentation of expenses not only ensures accurate tax filing but also prepares the business for potential audits. In the event of an audit, having well-organized records can expedite the process and demonstrate compliance.
Understanding taxable income in MLM involves recognizing the components of gross income, distinguishing between retail profits and commissions, and diligently tracking deductible expenses.
Categorizing MLM Income for Tax Purposes
1. Self-Employment Income:
- Definition: If an individual in MLM operates as an independent contractor and receives income directly based on their sales and the sales of their downline, this income is often considered self-employment income.
- Implications: Self-employed individuals are responsible for both the employer and employee portions of Social Security and Medicare taxes. They may also be eligible for various business-related deductions.
2. Business Income:
- Definition: Some MLM participants may establish a formal business structure, such as a sole proprietorship or LLC, to conduct their MLM activities. In such cases, income earned is classified as business income.
- Implications: Business income may be subject to different tax treatments, and business-related expenses can be deducted from the income, potentially reducing the overall tax liability.
Implications of Each Classification for Tax Filing:
1. Self-Employment Income:
- Tax Responsibility: Individuals with self-employment income are responsible for filing Schedule C along with their personal tax return (Form 1040).
- Tax Implications: Self-employed individuals may be eligible for the Qualified Business Income (QBI) deduction and can deduct business-related expenses, such as advertising, supplies, and travel.
2. Business Income:
- Tax Responsibility: Those with formal business structures report their income and expenses on the respective business tax return forms, such as Schedule C for sole proprietorships or Form 1065 for partnerships.
- Tax Implications: Business income may be subject to specific tax rates, and allowable deductions depend on the business structure. Business owners can benefit from strategic tax planning and may have different retirement savings options.
Significance of Form 1099-NEC for MLM Income Reporting:
1. What is Form 1099-NEC?
- Definition: MLM companies are required to issue Form 1099-NEC to individuals who earn $600 or more in non-employee compensation during the tax year.
- Implications: This form is crucial for accurate income reporting and tax compliance.
2. Importance in MLM:
- Tracking Income: MLM participants should ensure they receive Form 1099-NEC from the MLM company, detailing their earnings.
- Reporting Income: The information on Form 1099-NEC is used to report income on the individual’s tax return. It helps verify the accuracy of reported income and assists in avoiding discrepancies.
3. Tax Compliance:
- IRS Requirement: MLM companies are obligated to report payments to individuals, and failure to comply with Form 1099-NEC requirements can result in penalties.
- Individual Responsibility: MLM participants must report all income, even if it’s below the $600 threshold, ensuring full compliance with tax regulations.
Tax Deductions and Expenses for MLM Businesses
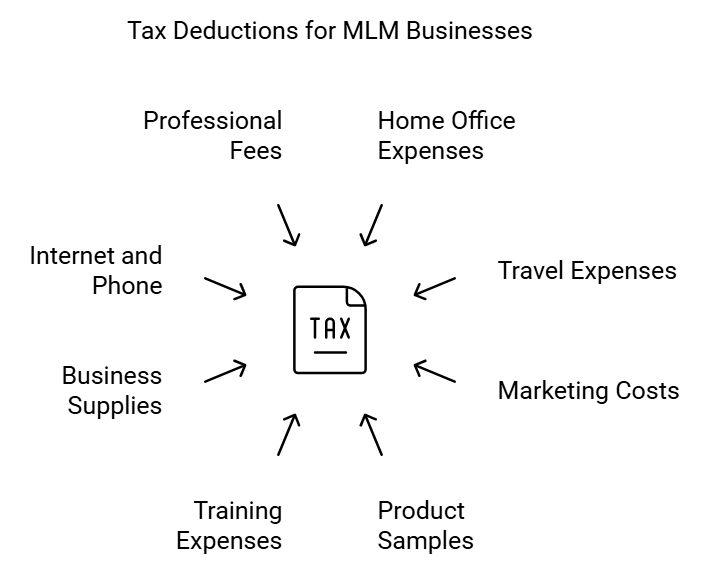
1. Home Office Expenses:
- Deductions: Portion of rent or mortgage interest, utilities, and property taxes directly related to the home office space.
- Requirements: The home office must be used regularly and exclusively for business purposes.
2. Travel Expenses:
- Deductions: Transportation costs, lodging, meals, and incidental expenses related to business travel.
- Requirements: Travel must be primarily for business purposes, with a documented business purpose for each expense.
3. Marketing Costs:
- Deductions: Expenses related to advertising, promotions, and marketing materials.
- Requirements: Deductions are allowed for costs directly associated with promoting and marketing the MLM business.
4. Product Samples and Inventory Costs:
- Deductions: Cost of product samples provided to potential customers, as well as the cost of purchasing and maintaining inventory.
- Requirements: Must be directly related to the MLM business and necessary for income generation.
5. Training and Education Expenses:
- Deductions: Costs associated with training sessions, conferences, and educational materials relevant to the MLM business.
- Requirements: Expenses must be directly tied to improving skills and knowledge in the MLM industry.
6. Business Supplies:
- Deductions: Costs of office supplies, business cards, and any other materials necessary for running the MLM business.
- Requirements: Supplies must be used exclusively for business purposes.
7. Internet and Phone Expenses:
- Deductions: A portion of internet and phone bills attributable to business use.
- Requirements: The percentage deducted should reflect the business-related use of these services.
8. Professional Fees:
- Deductions: Fees paid for professional services, such as accounting or legal advice related to the MLM business.
- Requirements: Services must directly contribute to the operation or improvement of the business.
Elaboration on Specific Deductions:
1. Home Office Expenses:
Home office deductions can significantly reduce taxable income for MLM entrepreneurs. Proper documentation and adherence to IRS guidelines are crucial.
2. Travel Expenses:
MLM businesses often involve travel for meetings, conferences, and training. Keeping detailed records of expenses and the business purpose is essential for claiming deductions.
3. Marketing Costs:
Marketing is integral to MLM success. Deducting expenses related to advertising and promotions helps offset the costs of growing the business.
Emphasizing the Importance of Record-Keeping:
1. Accurate Documentation:
Thorough record-keeping is essential for substantiating deductions in case of an audit. Keep receipts, invoices, and documentation for all business-related expenses.
2. Organized Systems:
Implementing organized systems, whether digital or physical, for tracking expenses ensures that no deduction is overlooked and facilitates easy retrieval of information during tax filing.
3. Audit Preparedness:
Well-maintained records not only aid in tax filing but also make the audit process smoother if the IRS ever requests documentation.
4. Maximizing Deductions:
Proactive record-keeping helps MLM businesses maximize allowable deductions, ultimately reducing the overall tax liability and improving financial efficiency.
Understanding and leveraging tax deductions for MLM businesses is crucial for optimizing financial outcomes. Specific deductions like home office expenses, travel costs, and marketing expenses can significantly impact taxable income.
The importance of meticulous record-keeping cannot be overstated, as it serves as a foundation for accurate and compliant tax management in the dynamic world of MLM.
How to File Taxes for MLM Business
1. Gather Necessary Documents:
- Collect all relevant financial documents, including Form 1099-NEC from the MLM company, records of income, and receipts for business expenses.
2. Determine Business Structure:
- Identify whether your MLM business operates as self-employment or through a formal business structure (e.g., sole proprietorship, LLC).
3. Complete Schedule C (Form 1040):
- For Self-Employed Individuals:
- Use Schedule C (Profit or Loss from Business) to report MLM income and deductible business expenses.
- Enter gross income and subtract allowable expenses to calculate net profit or loss.
4. Report Income on Form 1040:
- Transfer the net profit or loss from Schedule C to the appropriate section of Form 1040 (U.S. Individual Income Tax Return).
5. Consider Deductions and Credits:
- Explore eligible deductions and tax credits to minimize taxable income. Common deductions include home office expenses, travel costs, and marketing expenses.
6. Understand Estimated Tax Payments:
- Estimate your annual tax liability and make quarterly estimated tax payments using Form 1040-ES to avoid underpayment penalties.
7. File State Taxes:
- If applicable, file state income taxes based on your MLM business income. Follow the state’s specific tax forms and guidelines.
8. Keep Detailed Records:
- Maintain thorough and organized records of income, expenses, and any supporting documentation. This is crucial for potential audits and accurate tax filing.
9. Consider Professional Assistance:
- Consult with a tax professional or accountant experienced in small businesses and MLMs for personalized advice and guidance.
Role of Schedule C and Form 1040:
1. Schedule C (Profit or Loss from Business):
- Purpose: Used to calculate net profit or loss from business activities, including MLM income and deductible expenses.
- Steps:
- Enter gross income from MLM activities.
- Deduct allowable business expenses.
- Calculate net profit or loss.
2. Form 1040 (U.S. Individual Income Tax Return):
- Purpose: The main tax form for reporting personal income.
- Steps:
- Transfer net profit or loss from Schedule C to the appropriate section.
- Include other sources of income and deductions.
- Calculate total taxable income and determine the tax liability.
Significance of Making Estimated Tax Payments:
1. Avoid Underpayment Penalties: Making estimated tax payments quarterly helps avoid penalties for underpayment, ensuring compliance with tax regulations.
2. Manage Cash Flow: Distributing tax payments throughout the year helps manage cash flow, preventing financial strain during the tax filing season.
3. Accurate Budgeting: Estimated tax payments facilitate more accurate budgeting by allowing business owners to plan for their tax obligations.
4. Minimize Year-End Surprises: Regular estimated payments prevent surprises during tax season and provide a clearer picture of the business’s financial health.
Filing taxes for an MLM business involves a systematic process, utilizing Schedule C and Form 1040 to report income and deductions accurately. Making estimated tax payments throughout the year is a proactive strategy to ensure compliance and manage the financial aspects of the MLM business efficiently.
MLM Tax Worksheet Template
An MLM (Multi-Level Marketing) tax worksheet helps MLM participants (distributors or affiliates) organize and calculate their taxes by keeping track of income, expenses, and deductions. As an MLM distributor, you are considered self-employed, which means you’re responsible for reporting both your earnings and eligible business expenses to the IRS.
Here’s a simple MLM tax worksheet to help you get started:
1. Income:
- Commissions Earned: _________
- Bonuses Received: _________
- Retail Profit (Sales to Customers): _________
- Other Income (Gift Certificates, Overrides, etc.): _________
Total Income: $__________
2. Expenses:
List all expenses related to your MLM business. You can deduct many business-related costs that are necessary for running your business.
- Inventory/Products Purchased for Resale: _________
- Shipping/Handling Costs: _________
- Advertising and Marketing Expenses (e.g., social media ads, flyers, etc.): _________
- Home Office Expenses (percentage of rent or mortgage, utilities, etc.): _________
- Travel Expenses (mileage, airfare, lodging for business trips): _________
- Supplies and Materials (business cards, pens, etc.): _________
- Training and Education (seminars, books, online courses): _________
- Phone/Internet Costs (portion used for business): _________
- Software and Subscriptions (e.g., website hosting, email services): _________
- Membership Fees (for industry associations or MLM networks): _________
- Business Insurance: _________
- Other Business Expenses (be specific): _________
Total Expenses: $__________
3. Net Profit or Loss:
To calculate your net profit (or loss), subtract your Total Expenses from your Total Income.
- Net Profit/Loss:
- Income ($) – Expenses ($) = Net Profit/Loss ($__________)
4. Self-Employment Tax Calculation:
MLM distributors must pay self-employment tax (which covers Social Security and Medicare) on their net income. The self-employment tax rate is 15.3% on net earnings.
- Net Earnings from MLM: $__________
- Self-Employment Tax (15.3%): $__________ (multiply your net earnings by 0.153)
5. Federal Income Tax:
You also need to calculate your federal income tax based on your tax bracket. Keep track of any deductions and credits you may qualify for (e.g., standard deduction, itemized deductions, etc.).
- Taxable Income: $__________ (after deducting standard or itemized deductions)
- Estimated Federal Income Tax: _________ (based on tax bracket)
6. Estimated Tax Payments:
If you are required to make quarterly estimated tax payments, ensure you calculate those based on your net income. You can use IRS Form 1040-ES for guidance on estimated tax payments.
Summary:
- Total Income: $__________
- Total Expenses: $__________
- Net Profit/Loss: $__________
- Self-Employment Tax: $__________
- Estimated Federal Income Tax: $__________
- Total Tax Liability: $__________ (sum of self-employment tax and federal income tax)
Conclusion
Navigating the tax landscape for your MLM business is a crucial aspect of maintaining financial health, compliance, and long-term sustainability. By understanding the specific considerations outlined in this guide, MLM entrepreneurs can approach the tax filing process with confidence in 2024. From categorizing income to leveraging allowable deductions, each step contributes to a comprehensive and strategic approach to managing taxes within the dynamic realm of network marketing.
As the tax season approaches, MLM business owners should empower themselves with the knowledge and tools needed to navigate the complexities of tax filing successfully. Consulting with tax professionals, staying abreast of regulatory changes, and maintaining a commitment to financial transparency will not only ensure compliance but also position your MLM venture for continued growth and success in the ever-evolving landscape of network marketing. Remember, an informed approach to taxes is not just a legal necessity but a strategic investment in the sustained prosperity of your MLM business.


