Complete Guide to Sales Tax in San Antonio TX (2024)
Welcome to San Antonio, Texas, a city where history and modernity converge. As you immerse yourself in its cultural tapestry, it’s essential to grasp the current sales tax landscape in 2024. San Antonio’s dynamic economic pulse is reflected in its sales tax rates, influencing every purchase made within its vibrant markets.
Whether you’re a local navigating daily transactions or a visitor exploring its unique offerings, understanding these rates ensures a smoother shopping experience. Join us as we unravel the specifics of San Antonio’s sales tax, enhancing your journey through the heart of this energetic and welcoming Texan city.
Understanding the Basics of Sales Tax in Texas
Navigating the intricate world of sales tax in Texas requires a comprehensive understanding of its fundamental components. Let’s delve into the details:
1) State Rate
- Uniform Foundation: The state rate forms the bedrock of Texas sales tax, applying consistently across the entire state.
- Percentage Basis: Represented as a percentage, this rate influences the taxable amount of a wide array of goods and services.
2) Local Rates
- Regional Variability: Counties and municipalities have the authority to augment the state rate with local rates, resulting in a diverse tax landscape.
- Varied Taxation: Local rates can fluctuate, impacting the overall sales tax burden based on the specific jurisdiction of the transaction.
3) Special Rates
- Designated Purposes: Some jurisdictions implement special rates earmarked for particular purposes such as infrastructure projects, public services, or local initiatives.
- Focused Impact: These special rates allow communities to tailor their taxation to address specific needs or fund targeted projects.
4) Exemptions
- Diverse Exclusions: Certain items and services enjoy exemptions from sales tax, ranging from essential goods to industry-specific products.
- Complex Landscape: The list of exemptions is extensive and nuanced, contributing to the complexity of the Texan sales tax system.
By unraveling the intricacies of these components, individuals and businesses can gain a nuanced understanding of the multifaceted sales tax structure in Texas, enabling informed decision-making in various transactions.
Different Types of Businesses Subject to Sales Tax Collection and Reporting
In the diverse commercial landscape, various types of businesses shoulder the responsibility of sales tax collection and reporting. Understanding the breadth of these enterprises is crucial for compliance and financial management:
1) Retail Businesses
- Brick-and-Mortar Retailers: Traditional physical stores selling goods directly to consumers.
- Online Retailers: E-commerce platforms and online marketplaces engaging in sales transactions.
2) Service Providers
- Professional Services: Businesses offering services such as consulting, legal advice, or accounting.
- Personal Care Services: Salons, spas, and wellness centers provide personal care services.
3) Hospitality and Entertainment
- Restaurants and Cafes: Establishments offering food and beverages for immediate consumption.
- Event Venues: Businesses hosting events, concerts, or conferences that involve ticket sales.
4) Manufacturing and Wholesale
- Manufacturers: Companies involved in the production and sale of tangible goods.
- Wholesalers: Businesses selling products in bulk to retailers or other businesses.
5) Construction and Contractors
- Construction Companies: Engaged in the construction of buildings or infrastructure projects.
- Contractors: Individuals or companies providing specialized services within the construction industry.
6) Transportation and Delivery Services
- Delivery Services: Companies involved in the delivery of goods, whether through traditional means or gig economy platforms.
- Transportation Companies: Businesses providing transportation services, such as taxis or rideshare services.
7) Rental Services
- Equipment Rental: Businesses renting out tools, machinery, or other equipment.
- Property Rental: Owners of residential or commercial properties engaged in leasing.
Each of these business categories plays a distinctive role in the economic ecosystem, and their engagement in sales tax collection and reporting is vital for maintaining compliance with local and state regulations. Understanding the specific obligations associated with each business type is essential for accurate financial management and adherence to legal requirements.
Demystifying the San Antonio Sales Tax Rate
In the vibrant city of San Antonio, demystifying the sales tax rate is essential for both residents and businesses. Let’s unravel the intricacies of the San Antonio sales tax landscape, providing clarity on its components and implications.
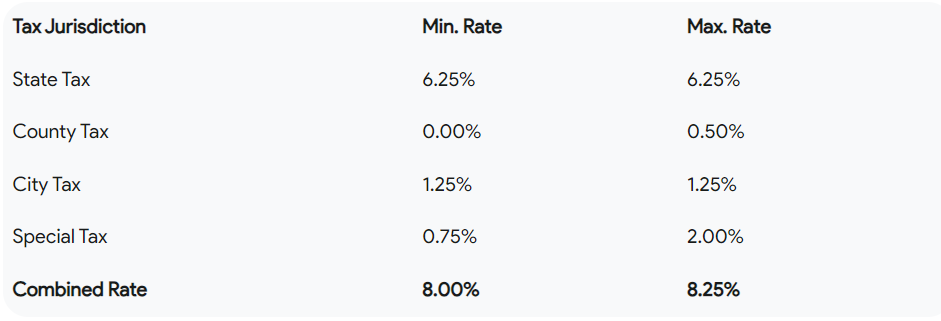
1) Base State Rate:
- At the core lies the base state rate, a percentage applied uniformly across Texas.
- Understanding this foundational rate is crucial for comprehending the starting point of sales tax calculations in San Antonio.
2) Local Additions:
- Beyond the state rate, local jurisdictions, including San Antonio, may add their own rates.
- Exploring these local additions is key to grasping the total sales tax rate applicable in specific areas within the city.
3) Special Taxes and Districts:
- San Antonio may have special taxes or districts with unique rates designated for specific purposes.
- These can include taxes earmarked for local projects, infrastructure improvements, or economic development initiatives.
4) Exemptions and Considerations:
- Certain items and services may enjoy exemptions from sales tax in San Antonio.
- Navigating these exemptions is vital for businesses and consumers alike to ensure accurate and compliant transactions.
5) E-commerce and Remote Sellers:
- With the rise of e-commerce, businesses operating remotely may also be subject to San Antonio’s sales tax.
- Understanding the implications of online transactions is crucial in the ever-evolving landscape of digital commerce.
6) Impact on Businesses:
- For businesses, compliance with the San Antonio sales tax rate is paramount to avoid legal complications.
- Staying informed about changes in rates and regulations ensures smooth and lawful operations within the city.
Demystifying the San Antonio sales tax rate involves unraveling the layers of state, local, and special taxes, as well as considering exemptions and the impact on businesses, making it possible for residents and entrepreneurs alike to navigate the local economic landscape with confidence.
Demystifying the San Antonio Sales Tax Rate
In the vibrant city of San Antonio, demystifying the sales tax rate is essential for both residents and businesses. Let’s unravel the intricacies of the San Antonio sales tax landscape, providing clarity on its components and implications.
1) Base State Rate:
- At the core lies the base state rate, a percentage applied uniformly across Texas.
- Understanding this foundational rate is crucial for comprehending the starting point of sales tax calculations in San Antonio.
2) Local Additions:
- Beyond the state rate, local jurisdictions, including San Antonio, may add their own rates.
- Exploring these local additions is key to grasping the total sales tax rate applicable in specific areas within the city.
3) Special Taxes and Districts:
- San Antonio may have special taxes or districts with unique rates designated for specific purposes.
- These can include taxes earmarked for local projects, infrastructure improvements, or economic development initiatives.
4) Exemptions and Considerations:
- Certain items and services may enjoy exemptions from sales tax in San Antonio.
- Navigating these exemptions is vital for businesses and consumers alike to ensure accurate and compliant transactions.
5) E-commerce and Remote Sellers:
- With the rise of e-commerce, businesses operating remotely may also be subject to San Antonio’s sales tax.
- Understanding the implications of online transactions is crucial in the ever-evolving landscape of digital commerce.
6) Impact on Businesses:
- For businesses, compliance with the San Antonio sales tax rate is paramount to avoid legal complications.
- Staying informed about changes in rates and regulations ensures smooth and lawful operations within the city.
Demystifying the San Antonio sales tax rate involves unraveling the layers of state, local, and special taxes, as well as considering exemptions and the impact on businesses, making it possible for residents and entrepreneurs alike to navigate the local economic landscape with confidence.
Here’s a list of commonly sold goods and services in San Antonio, indicating their general tax status:
Taxable Goods and Services:
- Clothing and Accessories: Taxable
- Electronics (e.g., laptops, smartphones): Taxable
- Furniture and Home Decor: Taxable
- Books and Magazines: Taxable
- Appliances (e.g., refrigerators, washing machines): Taxable
- Jewelry: Taxable
- Restaurant Meals: Taxable
- Takeout and Delivery Food: Taxable
- Hotel Accommodations: Taxable
- Movies and Concert Tickets: Taxable
- Maintenance and Repair Services: Taxable (e.g., car repairs, appliance repairs)
Exempt Goods and Services:
- Groceries: Exempt
- Prescription Medications: Exempt
- Medical Services: Exempt
- Educational Services: Exempt
- Non-Profits Charitable Sales: Exempt
- Certain Clothing Items (e.g., work uniforms): Exempt
- Agricultural Equipment: Exempt
- Residential Energy Services: Exempt
- Childcare Services: Exempt
- Legal Services: Typically Taxable, but exemptions may apply in specific cases
Grey Areas or Special Considerations:
- Prepared Food (e.g., hot deli items): Taxable in some cases
- Digital Goods (e.g., software, e-books): Taxability can vary
- Hybrid Products (e.g., decorative items with a functional purpose): Tax status may depend on primary use
Remember, this list is not exhaustive, and specific items or services may have unique tax considerations. Businesses and consumers must stay informed about changes in tax laws and regulations to ensure accurate transactions and compliance with San Antonio’s sales tax requirements.

Compliance and Reporting Requirements for San Antonio Businesses
Operating a business in San Antonio comes with specific compliance and reporting obligations to ensure adherence to local and state regulations. Navigating these requirements is essential for maintaining legal standing and fostering a transparent business environment.
1) Sales Tax Collection and Reporting:
- Sales Tax Permit: Businesses engaging in retail sales must obtain a sales tax permit from the Texas Comptroller of Public Accounts.
- Accurate Collection: Ensure the correct collection of sales tax on taxable transactions.
- Timely Reporting: Submit regular sales tax reports, typically on a monthly or quarterly basis.
2) Recordkeeping:
- Documentation: Maintain comprehensive records of sales transactions, purchases, and expenses.
- Retention Period: Adhere to the prescribed retention period for financial records, typically several years.
3) Employee Taxes:
- Payroll Taxes: Deduct and remit federal and state payroll taxes.
- Unemployment Taxes: Contribute to state unemployment taxes.
4) Business Permits and Licenses:
- Local Business Permits: Obtain necessary permits from the City of San Antonio or Bexar County, depending on the business’s location and nature.
- Industry-Specific Licenses: Certain industries may require additional licenses or certifications.
5) Income Tax Filings:
- Federal Income Tax: File annual federal income tax returns with the Internal Revenue Service (IRS).
- State Income Tax: Texas does not impose state income tax, but businesses may be subject to other state taxes.
6) Compliance with Local Regulations:
- Zoning Laws: Adhere to local zoning regulations and land use requirements.
- Environmental Regulations: Comply with environmental regulations relevant to the business’s operations.
7) Employee Regulations:
- Labor Laws: Ensure compliance with federal and state labor laws, including minimum wage and overtime regulations.
- Worker’s Compensation: Provide and maintain worker’s compensation insurance as required.
8) Health and Safety Compliance:
- Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA): Follow OSHA regulations to maintain a safe workplace.
- Health Department Compliance: Adhere to health department regulations if applicable to the business.
9) Annual Reports and Renewals:
- File Annual Reports: Submit required annual reports to the appropriate authorities.
- Renewals: Renew business licenses and permits as necessary.
10) Stay Informed and Seek Professional Advice:
- Regular Updates: Stay informed about changes in tax laws, regulations, and compliance requirements.
- Consult Professionals: Seek guidance from accountants, tax professionals, and legal advisors to ensure ongoing compliance.
By diligently addressing these compliance and reporting requirements, businesses in San Antonio can navigate the regulatory landscape effectively, promoting a sound and sustainable operational foundation.
Sales tax permits required for various business activities in San Antonio
In San Antonio, as in the state of Texas, businesses engaging in various activities may need specific sales tax permits to comply with legal requirements. The main sales tax permit is issued by the Texas Comptroller of Public Accounts, but additional permits may be necessary depending on the nature of the business. Here are different types of sales tax permits that businesses in San Antonio might need:
1) Texas Sales and Use Tax Permit:
- Requirement: All businesses engaging in selling tangible personal property in Texas are generally required to have a Texas Sales and Use Tax Permit.
- Application: Obtainable through the Texas Comptroller of Public Accounts website.
2) Sales Tax Permit for Out-of-State Sellers:
- Requirement: Businesses located outside Texas but making sales into the state may need a permit if they meet certain economic thresholds.
- Application: Also obtained through the Texas Comptroller of Public Accounts.
3) Temporary Event Sales Tax Permit:
- Requirement: Vendors participating in temporary events, such as fairs, markets, or festivals, may need a temporary event sales tax permit.
- Application: Applied for specifically for the duration of the event through the Texas Comptroller’s office.
4) Direct Payment Permit:
- Requirement: Certain businesses that frequently make tax-exempt purchases for resale may qualify for a Direct Payment Permit.
- Application: Applied for through the Texas Comptroller’s office.
5) Sales Tax Permit for Agricultural and Timber Exemption:
- Requirement: Agricultural and timber producers may need a specific permit for exemption from sales tax on certain purchases.
- Application: Obtained through the Texas Comptroller’s office.
6) Texas Taxpayer ID Number:
- Requirement: In addition to the sales tax permit, businesses often need a Texas Taxpayer ID Number for various tax-related purposes.
- Application: Applied for through the Texas Comptroller’s office.
It’s essential for businesses in San Antonio to carefully assess their activities and determine which permits are necessary for compliance with state and local regulations. The Texas Comptroller of Public Accounts website provides detailed information and resources for businesses to apply for and manage their sales tax permits. Additionally, seeking advice from tax professionals can help ensure that businesses obtain all the required permits for their specific operations.
Frequency and Methods for Filing Sales Tax Returns in San Antonio
Compliance with sales tax regulations in San Antonio involves the timely filing of sales tax returns, and understanding the frequency and available methods is crucial for businesses. Here’s a breakdown of the key aspects:
1) Frequency of Sales Tax Filings:
- Monthly Filing: Businesses with higher sales volumes or those mandated by the state may be required to file monthly.
- Quarterly Filing: Businesses with moderate sales volumes may file every quarter.
- Annual Filing: Some small businesses with minimal sales may be eligible for annual filing.
2) Methods for Filing Sales Tax Returns:
- Online via WebFile: The Texas Comptroller of Public Accounts provides an online portal called WebFile for businesses to file their sales tax returns electronically. This is the most common and recommended method.
- TEXNET (Electronic Funds Transfer): Businesses can use TEXNET to submit electronic payments for the sales tax due along with their return.
- Paper Filing: While electronic filing is encouraged, businesses may have the option to file paper returns if electronic methods are not feasible.
3) Electronic Filing Options:
- WebFile: The WebFile system allows businesses to file and pay their sales tax electronically. It is a secure and user-friendly online platform.
- Electronic Data Interchange (EDI): Larger businesses with complex reporting needs may opt for EDI, a method of exchanging data electronically with the Texas Comptroller’s office.
- Third-Party Software: Businesses can use approved third-party software that interfaces with the Texas Comptroller’s systems to streamline the filing process.
4) Important Considerations:
- Timely Filing: Adhering to the designated filing frequency is crucial to avoid penalties and interest.
- Payment Methods: Electronic payments can be made through various methods, including credit/debit cards or electronic funds transfers.
5) Benefits of Electronic Filing:
- Efficiency: Electronic filing reduces processing time and potential errors associated with manual filings.
- Accuracy: The online systems often have built-in checks to help ensure accurate reporting.
- Confirmation Receipt: Businesses receive confirmation of the filing, providing a record of compliance.
It’s imperative for businesses to stay informed about their specific filing requirements based on their sales volume and to utilize the electronic filing options provided by the Texas Comptroller for a streamlined and efficient process.
Penalties and Interest for Late or Inaccurate Filings in San Antonio
Ensuring timely and accurate filing of sales tax returns in San Antonio is not only a legal obligation but also a crucial aspect of maintaining financial integrity. Failure to comply with filing deadlines or inaccuracies in reporting can result in significant penalties and interest. Here’s an overview emphasizing the importance of compliance:
1) Late Filing Penalties:
- Fixed Penalties: San Antonio imposes fixed penalties for each period that a return is filed late.
- Percentage of Tax Due: In addition to fixed penalties, businesses may face a percentage-based penalty on the amount of tax due.
2) Interest on Late Payments:
- Accrual of Interest: Interest accrues on any outstanding sales tax amounts from the due date until the date of payment.
- Compounded Interest: Interest is often compounded, meaning it is calculated not only on the principal amount but also on previously accrued interest.
3) Inaccurate or Fraudulent Filings:
- Penalties for Inaccuracies: Fines may be imposed for inaccuracies in reporting, such as understating sales or claiming incorrect deductions.
- Fraud Penalties: Deliberate attempts to defraud the tax system may lead to more severe penalties, including fines and legal consequences.
4) Criminal Charges:
- Willful Non-Compliance: Persistent and willful non-compliance can lead to criminal charges, resulting in fines and potentially imprisonment.
5) Importance of Timely and Accurate Reporting:
- Financial Consequences: Late or inaccurate filings can lead to increased financial burdens due to penalties and interest.
- Legal Consequences: Non-compliance may result in legal action, negatively impacting the reputation and viability of a business.
- Avoiding Compounding Issues: Timely and accurate reporting helps prevent compounding issues, allowing businesses to focus on growth rather than remediation.
6) Resources for Compliance:
- Educational Materials: The Texas Comptroller’s office provides resources and educational materials to assist businesses in understanding their filing obligations.
- Professional Advice: Seeking advice from tax professionals can help businesses navigate complex tax regulations and avoid costly mistakes.
7) Mitigating Penalties:
- Voluntary Disclosure Program: In some cases, businesses may be eligible for the Voluntary Disclosure Program, which allows them to voluntarily come forward to correct past errors with reduced penalties.
The consequences of late or inaccurate filings extend beyond financial penalties, impacting a business’s overall well-being. Therefore, it is paramount for businesses in San Antonio to prioritize compliance, leverage available resources, and seek professional advice to ensure accurate and timely reporting of sales tax obligations.
Are you currently doing your own books for your business?
Conclusion
In conclusion, successfully navigating San Antonio’s sales tax landscape requires businesses and individuals to prioritize compliance. From obtaining the necessary permits to embracing electronic filing options, attention to detail is paramount. Late or inaccurate filings can result in financial and legal consequences, underscoring the importance of staying informed.
By proactively engaging with available resources and fostering a culture of compliance, businesses contribute to a transparent and responsible economic environment, ensuring the continued success of San Antonio’s dynamic marketplace.


